Immune System Fun Facts: The immune system comprises all the cells, tissues, and organs that provide defense and protect the human body against pathogen attack. A pathogen is any particle that is foreign to the body and that can cause an infection.
The immune system is broadly divided into two types – the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system. The former is present in the human body since birth and provides the first line of defense against foreign pathogens and microbes.
The latter is acquired during life and growing up by encountering different pathogens and microbes and keeping track of or remembering the event. When a second such event occurs, the immune system has already acquired the means to combat the previously encountered pathogens, thereby preventing the infection. This concept is the basis for developing and creating vaccines.
Top 25 Immune System Fun Facts
Here are some of the interesting immune system fun facts:
1. The human body cannot survive without the immune system.
 The immune system provides both inherent and acquired states of immunity against attaching of foreign pathogens to the human body.
The immune system provides both inherent and acquired states of immunity against attaching of foreign pathogens to the human body.- Without the immune system, the human body can develop infections that can spread to different organs and organ systems resulting in a fatality.
- Certain cancers arise due to the dysfunction of the body’s immune system.
![]()
2. Illnesses were attributed to four senses of humor.
Historically speaking, before the discovery of the immune system, illnesses were attributed to four senses of humor.
 All illnesses of the body and mind, historically, were attributed to something known as “humor. “.
All illnesses of the body and mind, historically, were attributed to something known as “humor. “.- These humors, known as “melancholic“, “Phlegmatic“, “choleric“, or “sanguine“, were brought up by the Greek philosopher Hippocrates.
- They are linked to the four elements which represent bodily fluids: earth (black bile), air (blood), water (phlegm), and fire (yellow bile). physicians would diagnose illnesses based on the combination of these.
![]()
3. The most important part of the Immune system is the blood cells.
 The blood cells are the basis for the development and functioning of the immune system.
The blood cells are the basis for the development and functioning of the immune system.- The white blood cells form the precursors of the immune cells such as leukocytes, lymphocytes, and the antibodies that help protect the body from the attack of foreign pathogens.
- Immune cells are specialized blood cells of different types, such as phagocytes, T-cells, and B-cells. Some are produced in the thymus, whereas others are produced in the spleen and the lymph node.
![]()
4. The immune cells are always on surveillance.
 Immune cells circulate throughout the body via the blood and are also present in the tissues and organ systems.
Immune cells circulate throughout the body via the blood and are also present in the tissues and organ systems.- These immune cells allow for continued surveillance in the body and act as the primary defense against foreign pathogens.
![]()
5. Appendix is crucial for the immune system.
The appendix, thought to be a vestigial organ, may have an immune function.
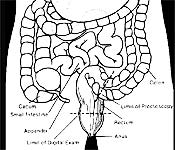 The appendix was long thought to be a vestigial organ that does not seem to serve any purpose in the functioning of the human body.
The appendix was long thought to be a vestigial organ that does not seem to serve any purpose in the functioning of the human body.- However, recent research has shed some light on what may be the actual function of the appendix.
- The appendix seems to house immune systems called Innate lymphoid cells (ILC) that help repopulate the gut microbiota following an infection or a course of antibiotics.
![]()
6. Some people have little or no immune system in the body.
 A genetic disease is known as SCID, or severe combined immunodeficiency disease results in the absence of immune cells that makes the affected susceptible to the attack of foreign pathogens and infections.
A genetic disease is known as SCID, or severe combined immunodeficiency disease results in the absence of immune cells that makes the affected susceptible to the attack of foreign pathogens and infections.- Various treatments for SCID have been developed, such as the transplant of bone marrow from a related individual or a sibling that helps restore the affected individual’s immune system.
![]()
7. Insomnia deteriorates the immune system.
Inadequate hours of sleep regularly hinders the functioning of the Immune system.
 Research shows that the immune system fails to function to its fullest capacity under the circumstances of lack of adequate sleep.
Research shows that the immune system fails to function to its fullest capacity under the circumstances of lack of adequate sleep.- Lack of sleep results in decreased proliferation of T cells that help provide immunity to the human body.
![]()
8. The human body produces many antibodies.
There are many different kinds of Antibodies produced by the immune system.
 Antibodies are immunoglobulins produced by the B-cells of the immune system. The B cells produce different kinds of antibodies.
Antibodies are immunoglobulins produced by the B-cells of the immune system. The B cells produce different kinds of antibodies.- Antibodies are fundamentally Y-shaped molecules that target pathogenic proteins and markers and attract other immune cells towards the pathogen for targeted destruction and elimination from the human body.
- Some of the antibodies of the immune system are IgA, IgG, IgE, IgD, etc.
![]()
9. The immune system can trigger harakiri within the self.
The immune system can be dysfunctional and can initiate an attack on the body itself.
 The immune system can sometimes dysfunction and target normal cells of the body.
The immune system can sometimes dysfunction and target normal cells of the body.- The disorders that arise from such an action are called Autoimmune disorders and are caused by both genetic and environmental factors.
- Type-2 diabetes is a type of autoimmune disorder that is caused by the body’s immune cells attacking its pancreatic islet cells, which leads to impaired production of insulin.
![]()
10. Bacteria in gut assists in the immune system.
 The gut houses colonies of healthy bacteria that maintain balance and helps in the production of vitamins such as vitamin B and vitamin K.
The gut houses colonies of healthy bacteria that maintain balance and helps in the production of vitamins such as vitamin B and vitamin K.- Depletion of the gut bacteria due to infections and antibiotics causes an imbalance that in turn causes a vitamin deficiency and reduced functioning of the immune system.
- The bacteria also help produce antibodies and help the immune system distinguish between self and foreign bodies.
![]()
11. Each part of the immune system has a unique function.
 The immune system comprises various components that have different functions in the human body.
The immune system comprises various components that have different functions in the human body.- The T and B lymphocytes are a type of lymphocyte involved in T-cell mediated killing of pathogenic cells and producing antibodies, respectively.
- On the other hand, natural killer cells, a type of T cells, have their targeted pathogenic killing method. Phagocytes and macrophages, such as skin, are present in different parts of the human body that phagocytose pathogenic material.
![]()
12. Vaccine – Great teacher to the immune system.
A vaccine is an essential tool that helps educate the immune system.
 Vaccines contain whole or part of the microorganism that causes the infection to induce the calm state of the infection in the body.
Vaccines contain whole or part of the microorganism that causes the infection to induce the calm state of the infection in the body.- The remnants of this vaccine-induced infection cycle are stored in the memory of cells called memory cells which are a type of B lymphocytes.
- When the human body encounters the pathogen a second time, the memory B cells spring into action and eliminate the pathogen, even before it can cause a full-fledged infection.
![]()
13. The human body hosts various types of bacteria.
Different kinds of bacteria are present in the human body, but all are not pathogenic.
 The human body encompasses a wide variety of microorganisms that are beneficial to the system.
The human body encompasses a wide variety of microorganisms that are beneficial to the system.- Gut microbiota help in maintaining a balance and providing nutrients.
- Bacteria present on the skin’s surface produce substances that kill other pathogenic microorganisms.
![]()
14. Stress negatively affects the function of the immune system.
 Stress releases steroid hormones such as cortisol that affects the functioning of the immune system.
Stress releases steroid hormones such as cortisol that affects the functioning of the immune system.- On the other hand, positive emotions and a healthy lifestyle boost the functioning of the immune system by helping lymphocyte proliferation.
![]()
15. Allergies are immune systems’ reactions.
Allergies are caused by the immune system reacting to a non-pathogenic substance.
 Allergies are immune reactions to the entry of a foreign particle that is non-pathogenic, in the human body.
Allergies are immune reactions to the entry of a foreign particle that is non-pathogenic, in the human body.- These reactions result in fainting, hives, runny nose, or sinus issues.
- A typical example of allergens that cause such a reaction includes pollen, dust, or even edible items such as peanuts.
![]()
16. Too clean environment = weak immune system.
Over-sterilizing one’s surroundings lead to the development of a weak immune system.
 A surrounding or environment that is over-clean is likely to contain little to no pathogens or microbes.
A surrounding or environment that is over-clean is likely to contain little to no pathogens or microbes.- Living in an overly-sterile environment reduces the risk of these pathogens entering the human body.
- However, too much sterile environment results in a weakened immune system because the immune system does not get a chance to be primed against different kinds of microbes and organisms.
![]()
17. Phagocyte cells mimic the digestion process.
Phagocytes are cells that mimic “swallowing” to eliminate pathogenic material from the body.
 Phagocytes are the type of immune cells that engulf pathogenic particles that are foreign to the human body.
Phagocytes are the type of immune cells that engulf pathogenic particles that are foreign to the human body.- Phagocytes have a pair of structures that extend from the main cell body called “pseudopodia” that help in encircling the pathogenic particle.
- Once the particle is engulfed, they release digestive enzymes that help to break down the pathogen and eliminate it from the human body.
![]()
18. Human gut has 80% of the immune system.
Most of the immune system, around 80%, is found in the human gut.
 The microbiota present in the gut is responsible for the development of the immune system.
The microbiota present in the gut is responsible for the development of the immune system.- Immune cells are densely distributed through the lymphatic system and lymphatic tissue, which is primarily concentrated in the gut.
- The gut-associated lymphoid tissue or GALT is responsible for providing immunity from pathogens and bacteria that enter the body through the ingestion of food.
![]()
19. The first response to an infection is called inflammation.
 Inflammation is the immune system’s first response to entry of a foreign body or pathogen into the body.
Inflammation is the immune system’s first response to entry of a foreign body or pathogen into the body.- Inflammatory mediators include cells and chemical signals that help bring about the process of inflammation.
- A healthy inflammation process is rapid and fades away quickly after it has begun.
![]()
20. A fever indicates a working immune system.
 When a foreign pathogen enters the body, the immune system brings about the process of inflammation.
When a foreign pathogen enters the body, the immune system brings about the process of inflammation.- The inflammation ultimately leads to an increase in body temperature, commonly known as fever.
- This reaction is the immune’s system response to eliminate the pathogen from the body by increasing body temperature to make survival for the pathogen in the body difficult.
![]()
21. Vitamin D has a positive effect on the immune system.
 A diet low in vitamin D and reduced exposure to sunlight can have an impact on Vitamin D levels in the body.
A diet low in vitamin D and reduced exposure to sunlight can have an impact on Vitamin D levels in the body.- Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that helps enhance the function of the immune system.
- Low levels of vitamin D are commonly associated with immune dysfunction or low immunity.
![]()
22. High lymphocyte count means infection
A high lymphocyte count on a complete blood count test can indicate an infection in the body.
 Lymphocytes are blood cells that play an important role in the functioning of the immune system.
Lymphocytes are blood cells that play an important role in the functioning of the immune system.- There are different kinds of lymphocytes – primarily the B and T lymphocytes that form the two branches of the immune system – adaptive and innate.
- In adults, the normal lymphocyte count is between 1,000 and 4,800 lymphocytes in 1 microliter (µL) of blood. A count higher than this can indicate the presence of an infection in the body.
![]()
23. WBCs are just 1% in 5 liters of blood.
WBCs or white blood cells make up only 1 percent of the cells in 5 liters of blood in the human body.
 The blood is made up of WBCs, RBCs, and Platelets – each performing their function in the body.
The blood is made up of WBCs, RBCs, and Platelets – each performing their function in the body.- WBCs account for only a small percentage of the cells in the blood. However, that number is quite enough to provide immunity to the body against foreign pathogens.
- WBCs are between 5,000 and 10,000 counts per microliter of blood in the human body.
![]()
24. Laughter helps boost immune function in the body.
 Laughter helps release chemical stimulants in the brain, that bring down stress.
Laughter helps release chemical stimulants in the brain, that bring down stress.- Stress is a major cause of immune dysfunction, making one more susceptible to infections.
- Chemical stimulants such as dopamine are released during laughter, which stimulates the immune system.
![]()
25. Bone marrow is crucial for immune system development.
The bone marrow is very important for the development of the immune system.
 All blood cells arise from the bone marrow. They then differentiate into different types according to their functions.
All blood cells arise from the bone marrow. They then differentiate into different types according to their functions.- In some diseases, the bone marrow is unable to produce adequate quantities of blood cells, which can lead to improper or absent functioning of the immune system.
- In such cases, bone marrow from a donor match is essential to restore the functioning of the immune system in the affected individual.
![]()
The Immune system is an integral part of the human body that helps to protect it against various pathogens and microorganisms that can cause infections. The immune system has different kinds of cells with varied functions that provide primary and secondary lines of defense against pathogenic attacks.
This system can sometimes cause dysfunction and cause autoimmune disorders, where immune cells attack the body’s cells. Example of autoimmune disorders includes Type 2 Diabetes and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Adequate nutrition, sunlight, stress control, and exercise are required to keep the immune system functioning well, promoting a healthy body.
![]()