Cord Blood Banking Pros and Cons: Modern medical research is more centered towards the treatment of advanced and complex diseases such as AIDS and cancer through stem cells study.
Stem cells are the unspecialized biological cells present in adults as well as during the prenatal period of embryos during pregnancy.
These cells can replenish and develop into any specific cell of tissues when required by the living body.
In adults, stem cells are found in various tissues such as blood, bones, brain, skin, and liver. During the developmental stage of the fetus, the cord is linked between the developing baby and the mother.
This cord is an ultimate source of nourishment to the newly forming life. The blood of the cord is another highly populated source of stem cells.
The richly nourished blood of cord is banked by medical scientists and doctors as it can be served to fulfill numerous research and rehabilitation purposes.
However, it is not a risk-free process and holds its detriments. Let’s analyze the pros and cons of cord blood banking in detail below.
Table of Contents
- 10 Cord Blood Banking Pros
- 10 Cord Blood Banking Cons
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the pros and cons of cord blood banking?
- How is cord blood collected?
- What are the differences between a private bank and a public cord blood bank?
- Can umbilical cord blood stem cells be used for family members?
- What are the advantages of umbilical cord blood stem cells?
- Why choose to donate cord blood to a public bank?
- What are the cons of public cord blood banking?
- How can cord blood be used in stem cell transplants?
- How long can cord blood be stored?
- What is the role of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists in cord blood banking?
10 Cord Blood Banking Pros
Here are the top 10 pros or advantages of cord blood banking:
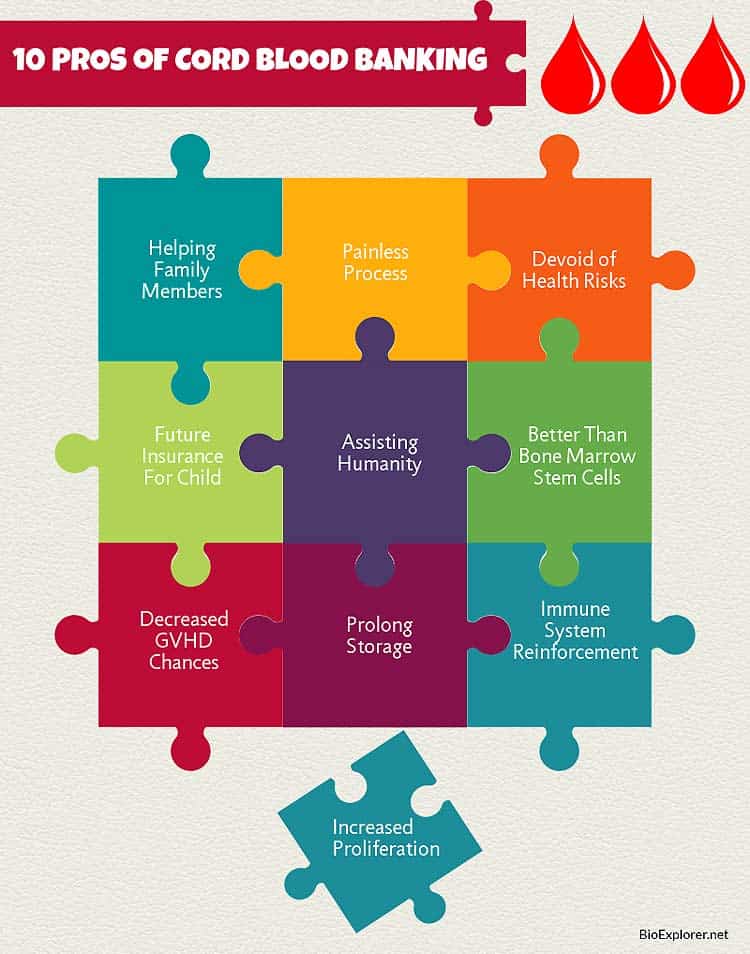
1. Helping Family Members
 In case of medical complications, provision of stem cells from a child could be a source of medical assistance to siblings, parents or any other family member, due to inheritance similarities.
In case of medical complications, provision of stem cells from a child could be a source of medical assistance to siblings, parents or any other family member, due to inheritance similarities.
- It is advisable to parents who afford to sustain the cost of the procedure to go for cord blood banking as it can provide medical relief to any family member in suffering.
2. Painless Process
 The procedure of collecting blood from the cord of a newly born baby is entirely non-technical and pain-free for the mother as well as the juvenile infant.
The procedure of collecting blood from the cord of a newly born baby is entirely non-technical and pain-free for the mother as well as the juvenile infant.
- The cord, the main channel linking the mother to the developing life, provides nutrients and a source of removing toxic wastes from the baby through the mother.
- After birth, before clamping the cord, it is cut about 10 inches apart, and blood is withdrawn into a bag or otherwise through a syringe.
- Both procedures are pain-free for the baby and the mother.
3. Devoid of Health Risks
 The banking of cord blood is a risk-free procedure for the baby and the mother.
The banking of cord blood is a risk-free procedure for the baby and the mother.
- Usually, the cord is folded and clamped after birth. It dries off a few weeks after birth. The blood is withdrawn from the cord after the baby gets delivered.
- The method does not give any post-procedure threat to the mother or infant baby and holds a total hazard free guarantee.
4. Future Insurance for Child
 The banking of cord blood provides safe and effective options to parents for saving their child’s health prospects.
The banking of cord blood provides safe and effective options to parents for saving their child’s health prospects.
- The process is regarded as similar to children’s health insurance. Due to the similarity in the genetic makeup of siblings and closely related family members, the saving of cord blood gives a safe choice to deal with any unhealthy future concerns.
- The process of saving stem cells holds a 100% chance of matching with the same individual and a 75% chance of similarity among the siblings.
5. Assisting Humanity
 The Food and Drugs Administration (FDA) appreciates couples to go for banking cord blood, even if they are not interested in the personalized usage of the miraculous blood.
The Food and Drugs Administration (FDA) appreciates couples to go for banking cord blood, even if they are not interested in the personalized usage of the miraculous blood.
- Due to increased chances of acceptance of stem cells into the foreign body, donor blood could prove to be an extraordinary relief to many sufferers.
- The donation of cord blood to public banks is motivated by the FDA as it can serve as an excellent transplantation option in many recipient patients.
6. Increased Effectiveness
 The stem cells from cord blood hold the uplift advantage of greater acceptability, decreased rejection and mismatching concerns than bone marrow stem cells.
The stem cells from cord blood hold the uplift advantage of greater acceptability, decreased rejection and mismatching concerns than bone marrow stem cells.
- The stem cells from bone marrow have remained an ultimate option of transplantation for years, despite the risks involved pre and post-transplantation.
- Better acceptability, fewer risks, and long shelf-life storage have made cord blood stem cells superior to bone marrow stem cells.
7. Decreased Chances of Graft Diseases
 The chances of graft diseases after transplantation are more with peripheral blood as compared to cord blood.
The chances of graft diseases after transplantation are more with peripheral blood as compared to cord blood.
- According to the National Institute of Health Sciences (NIH), chances of GVHD (Graft Versus Host Diseases) occur more commonly with grafts of peripheral blood.
- Due to the increased compatibility of donor and recipient in cord blood transplantation, chances of GVHD are decreased after the grafting in the host body.
8. Prolong Storage
 Apart from the easy collection of cord blood, it can be stored for almost 15 years.
Apart from the easy collection of cord blood, it can be stored for almost 15 years.
- When frozen, cord blood holds a longer shelf life for usage after many years of collection.
- On the contrary, bone marrow blood cannot be preserved longer.
- Bone marrow blood requires immediate transplantation after collection; otherwise, the blood loses efficacy and no longer remains viable to be used for transplantation purposes.
9. Immune System Reinforcement
 Nowadays, cord blood is widely used for boosting the immunity of patients, during the treatment of cancer.
Nowadays, cord blood is widely used for boosting the immunity of patients, during the treatment of cancer.
- Chemotherapeutic treatment of cancer negatively affects the immunity of the person.
- The researchers and medical scientists are employing the use of cord blood stem cells for increasing the strength of the immune system for better treatment outcomes and recovery.
10. Increased Proliferation Capability
 The stem cells from cord blood possess thriving response of division upon migration into the recipient body.
The stem cells from cord blood possess thriving response of division upon migration into the recipient body.
- Enhanced division capability of cord blood stem cells gives better results in recipients than peripheral stem cells.
- Being juvenile and greater proliferation, the yield of cord stem cells is about 14 times greater than cells from other sources.
10 Cord Blood Banking Cons
Now, let’s explore the cons or demerits of cord-blood banking:
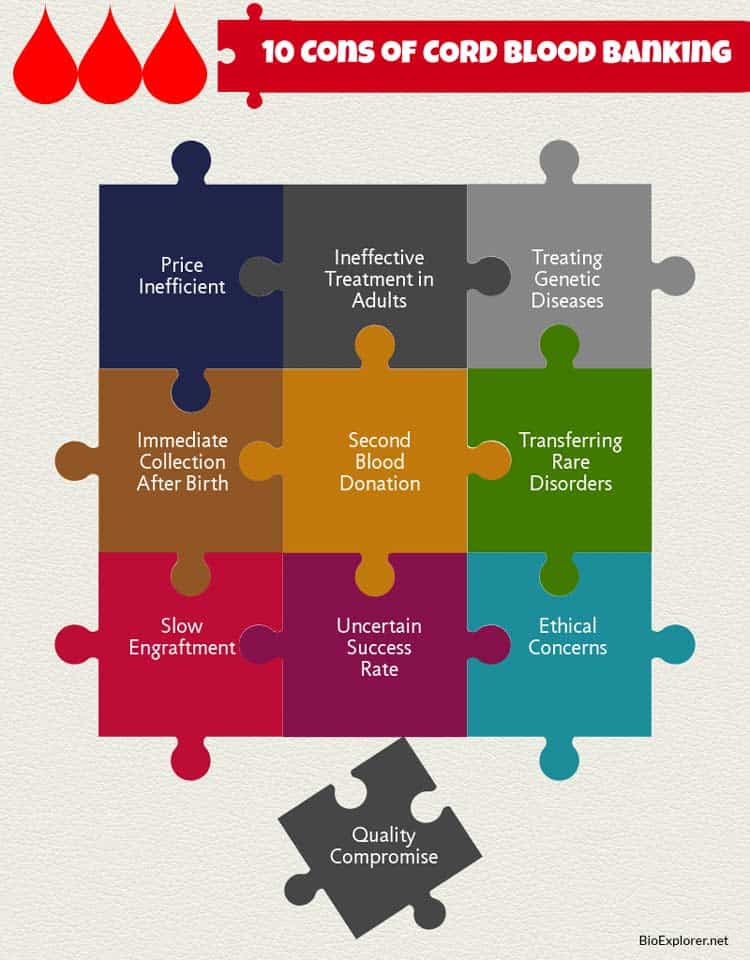
1. Price Inefficient
 Despite easier collection, the cord blood banking covers charges in two phases.
Despite easier collection, the cord blood banking covers charges in two phases.
- First, fees of about $2100 are charged regarding collection, enrolment, and storage for the primary year.
- Secondly, per annum, charges are taken for preservation.
- These charges make cord blood banking inefficient and unaffordable for many desiring families.
2. Ineffective Treatment in Adults
 The usage of cord blood for treatment in adults is considered an ineffective option.
The usage of cord blood for treatment in adults is considered an ineffective option.
- Because of the limited volume of cord blood available from the source, adults cannot be treated for ailments with much less quantity.
- Adults usually require greater blood volumes for treatment, which cannot be meant from the cord blood bank.
3. Autologous Transplantation
 Stem cells from a child are used to treat the diseases and ailments in the same child in autologous transplantation.
Stem cells from a child are used to treat the diseases and ailments in the same child in autologous transplantation.
- However, the method loses its credibility in the case of a child suffering from genetic diseases or blood cancer.
- Since the makeup of genes is similar for all body cells, stem cells can no longer remain viable to treat inherited diseases.
4. Immediate Collection
 Though, the cord blood banking is associated with the easier collection but requires immediate collection at the time of birth of a baby.
Though, the cord blood banking is associated with the easier collection but requires immediate collection at the time of birth of a baby.
- Couples going for cord blood baking need to decide way before delivery time, as cord blood banking cannot be decided in the spur of the delivery moment.
- Unlike the bone marrow stem cells for which the collection could take place at any time of life, umbilical cord stem cells are available for collection only at the time of birth.
5. Second Blood Donation
 Cord blood banking holds another disadvantage of lacking second donation chances.
Cord blood banking holds another disadvantage of lacking second donation chances.
- Stem cells from other sources can be replenished when required from the same source.
- However, the limited volume of blood is available in cord blood bank with no replenishment.
- Some other donor unit is taken in case of further requirement.
6. Transferring Rare Inherited Disorders
 The rare genetic diseases from the donor could get transferred to the recipient through cord blood banking.
The rare genetic diseases from the donor could get transferred to the recipient through cord blood banking.
- Inherited diseases cannot be assessed at the time of collection and manifest at later stages of life.
- Though the chances are quite low, cord blood poses a threat of transferring the genetic ailment through cord blood banking.
7. Slow Engraftment
 The cord blood stem cells show slow working in the recipient, after grafting.
The cord blood stem cells show slow working in the recipient, after grafting.
- The working of the graft is indicated by the appearance of specialized white blood cells (neutrophils and platelets) in the recipient’s blood.
- The white blood cells appear late in grafting from cord blood as compared to stem cells from bone marrow transplantation.
8. Uncertain Success Rate
 Based upon slow engraftment of umbilical cord stem cells, the certainty of the procedure remains questioned for months till the appearance of working symptoms.
Based upon slow engraftment of umbilical cord stem cells, the certainty of the procedure remains questioned for months till the appearance of working symptoms.
- The cord blood transplantation holds the ambiguous success of the procedure due to slow working.
- As a result, it also increases the chances of increased infections in recipients.
9. Ethical Concerns
 Usefulness of cord blood banking becomes gloomy under the ethical issues linked with the process.
Usefulness of cord blood banking becomes gloomy under the ethical issues linked with the process.
- FDA requires appropriate legal considerations and ethical consent of parents involved in cord blood banking.
- The privacy of donors and consent for research-based medical studies on umbilical cord stem cells is also requisite.
- The ethical issues linked with cord blood banking make it controversial under certain circumstances.
10. Quality Compromise
 The ability for long-term preservation of cord blood does not guarantee the quality of the stored specimen.
The ability for long-term preservation of cord blood does not guarantee the quality of the stored specimen.
- There is no assurance provided by the authorities that the specimen could retain its efficacy for a more extended period of duration or not in a frozen state.
- This problem raises concerns over the reliability of cord blood banking.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the pros and cons of cord blood banking?
The advantages of cord blood banking include using stem cells to treat diseases and genetic disorders and offering a type of “insurance” for the family’s health. However, its disadvantages involve the cost of private banking, ethical considerations, and the relatively low probability of a family member needing a stem cell transplant using their own stored cord blood.
How is cord blood collected?
Cord blood is collected immediately after the baby is born, and the umbilical cord is cut. The process involves using a sterile needle to collect the blood from the umbilical cord and placenta, ensuring no pain is caused to either the mother or the baby. This collected blood is then stored in a cord blood bank for future use.
What are the differences between a private bank and a public cord blood bank?
A private cord blood bank stores cord blood exclusively for use by the donor’s family, requiring a fee for collection and annual storage. On the other hand, a public cord blood bank stores donated cord blood that is available to anyone needing a stem cell transplant. Donating to a public bank is usually free, but using cord blood from a public bank may involve certain fees if a match is found.
Can umbilical cord blood stem cells be used for family members?
Yes, umbilical cord blood stem cells can be a valuable source for stem cell transplants for family members, especially siblings, as the likelihood of a match is higher within families. These transplants have been used to treat various diseases, including leukemia, lymphomas, and certain genetic disorders.
What are the advantages of umbilical cord blood stem cells?
The advantages of using umbilical cord blood stem cells include a rich source of hematopoietic stem cells, which can differentiate into all types of blood cells. This can play a critical role in treating blood-related diseases and certain cancers. Additionally, the collection process is safe, painless, and does not pose a risk to the mother or baby.
Why choose to donate cord blood to a public bank?
Donating cord blood to a public bank is a generous decision that can save lives. Donated cord blood that is stored in a public bank is made available to anyone in need of a stem cell transplant. This increases the diversity of the stem cell pool, enhancing the chances for patients worldwide to find matches.
What are the cons of public cord blood banking?
Cons of public cord blood banking include the potential for the donated blood not being available for direct use by the donor’s family as it enters a public repository. Additionally, despite stringent screening processes, there’s a rare risk of transmitting infections. The availability of a suitable match also cannot be guaranteed due to diverse genetic backgrounds.
How can cord blood be used in stem cell transplants?
Cord blood can be used in stem cell transplants by matching a needy patient with a cord blood unit with compatible human leukocyte antigens (HLAs). The stem cells are then administered to the patient, where they can repopulate the bone marrow, restore the blood cell counts, and potentially cure the underlying disease.
How long can cord blood be stored?
Cord blood can be stored for a long period, with some studies suggesting maintenance of cell viability for over 20 years. Proper storage conditions in a cord blood bank are critical for preserving the potency and effectiveness of the stem cells. Ongoing research aims to extend and ensure cord blood’s usability even further.
What is the role of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists in cord blood banking?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) provides guidelines and information to healthcare providers about cord blood banking, ensuring standardized practices in the collection, storage, and use of umbilical cord blood. ACOG supports informed decision-making by expecting parents to be educated on donating or privately banking cord blood.
![]()
Stem cell studies have revolutionized the management of critical illnesses and ailments. On-going research has increased the prospects of success in stem cell therapies.
Stem cells from the cord’s blood are considered a biological product by US Food and Drugs Administration (FDA) and are kept under strict observation.
Based upon the outcomes of cord blood banking, a couple (mother and father) should decide the procedure way before the birth of their child.
FDA encourages couples to go for cord blood banking as it could be a life-changing transplant for humanity.
![]()