Biomass Energy Pros and Cons: Biomass Energy is produced from organic materials which come from living organisms such as plants and animals. Fuel that is derived from the decomposition of organic material is also referred to as biomass fuel.
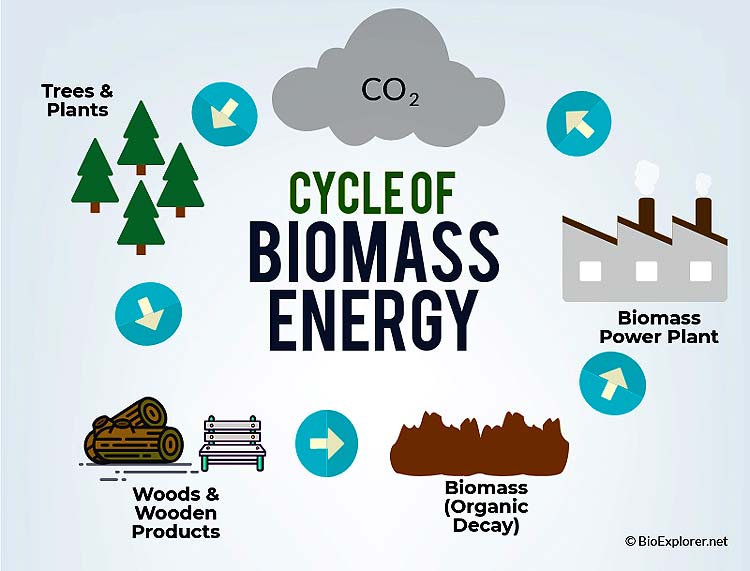
Table of Contents
The energy from this fuel, in turn, is used as the source of renewable and maintained production of other forms of energy such as electricity.
Biomass energy has both positive and negative aspects. Learn the biomass energy pros and cons on this page.
Top 10 Biomass Energy Pros
Let us review some of the advantages of biomass energy:
1. Un-depleteable Source of Energy

Renewable sources of energy are those who can get replenished even after usage.
- As it is known that biomass energy is produced from organic materials (i.e., dead plants, wood, organic garbage, and food waste), all these materials can be created again though not on a fast rate but still better than other sources.
- As a result, biomass fuel or energy is not under threat of getting depleted.
- This biomass fuel can be whether biogas or biofuel which can be used as conventional gas or fuel are usually used.
- It is essential to understand that biomass will remain un-deplete able as long as we maintain original plants and wood, and also manage all of the waste production.
- Until replantation and replenishment are made a habit, biomass will remain a renewable source of energy.
![]()
2. Feasibility For Sources of Fossil Fuels

Another major benefit of biomass energy is that it can reduce our dependence on nonrenewable fossil fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas. As global energy demand continues rising, our heavy reliance on finite fossil fuel reserves is unsustainable in the long run. By increasing our use of renewable biomass, we can supplement and potentially replace significant amounts of fossil fuel consumption.
- Fossil fuels are called non-renewable for good reason. Coal, oil and natural gas originated from prehistoric plants and animals that died over 280 million years ago. Over extremely long periods of time, heat and pressure transformed their remains into carbon-rich deposits buried deep underground. Importantly, this fossil fuel formation process stopped long ago – no new coal, oil or gas reserves are being created.
- At our current and growing rate of extraction, known global fossil fuel reserves may run out within the next 50-150 years. Oil is expected to be depleted first, with different estimates ranging from 2060 to 2090. Coal and natural gas may last a bit longer, but not indefinitely. Once fossil fuel resources are exhausted, they cannot be renewed on any timescale meaningful to human civilization.
- On the other hand, the stored solar energy in biomass can be renewed indefinitely. The carbon in fossil fuels has been trapped underground for millions of years, while the carbon in biomass is part of the natural above-ground carbon cycle. As plants and trees grow, absorbing carbon dioxide from the air, new biomass stock is constantly being generated. Utilizing biomass does not deplete the remaining fossil fuels underground.
- The more we transition from non-renewable fossil fuels to renewable bioenergy, the more we reduce the strain on finite reserves. Biofuels can directly replace liquid transport fuels like gasoline and diesel. Biogas can substitute for natural gas to provide heat and power. Biomass can be used instead of coal to generate electricity. Even partial replacement of fossil fuels with biomass derivatives makes the remaining fossil fuels last longer.
There are even carbon capture options where biomass energy facilities capture and sequester their carbon emissions. This results in net negative carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere.
Overall, biomass provides a renewable pathway for our energy needs that minimizes depletion of non-renewable fossil fuel reservoirs underground. With wise use of available biomass resources, we can extend the lifetime of remaining fossil fuels as we make the transition to true renewable energy dominance.
![]()
3. Better Environmental Conditions

Using biomass energy instead of fossil fuels provides major benefits in terms of reduced greenhouse gas emissions, especially carbon dioxide. Because biomass utilizes carbon that is part of the natural carbon cycle, it results in lower net emissions compared to releasing long-buried fossil carbon.
- The combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas releases ancient carbon into the atmosphere that has been locked underground for millions of years. This leads to a net increase in atmospheric CO2 levels that drives climate change. In contrast, the carbon released from burning biomass is carbon that was absorbed as these plants grew recently.
- When a new crop or tree grows, it absorbs CO2 from the air through photosynthesis and incorporates the carbon in its tissues. This carbon then gets released back into the atmosphere when biomass is combusted. Since this carbon was recently above ground and circulating in the biosphere, it does not upset the overall balance of the carbon cycle. The same amount of carbon was taken up during plant growth as is released by burning the biomass.
- In this way, biomass energy is considered carbon neutral. Its carbon emissions do not result in a net addition of CO2 to the atmosphere like fossil fuels. Short-term carbon cycling from biomass contrasts with the one-way transfer of buried carbon in fossils fuels that disturbs long-term carbon equilibrium.
- In fact, biomass goes beyond carbon neutral to actually carbon negative when combined with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology. CCS traps the CO2 emissions from biomass energy before they are released, so atmospheric CO2 is reduced. Since the biomass carbon came from the atmosphere in the first place, this achieves negative emissions. More CO2 is pulled from the air than emitted.
- Several lifecycle analyses have quantified the sizable climate benefit of substituting biomass for fossil fuels. One study found that generating electricity from biomass instead of coal reduced lifecycle emissions by over 90%. The displacement of oil-based transportation fuels with biofuels can cut net emissions by 65 to 80%.
Overall, increased utilization of biomass energy translates directly into lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Because it recycles carbon naturally, biomass promises major emissions reductions compared to mining and burning fossil fuels from the ground. Converting energy production to carbon-neutral biomass will bring us much closer to mitigating global climate change.
![]()
4. Diversified Usage

One of the great advantages of biomass is its versatility as an energy source.
- Biomass can be converted into various forms to produce power, heat, and liquid fuels that meet a wide range of energy needs. This flexibility allows biomass to be utilized in many more applications compared to fossil fuels.
- One major use of biomass is for producing liquid biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel. Ethanol derived from corn and other crops can be blended with gasoline to power cars and trucks. Biodiesel manufactured from vegetable oils and animal fats can replace conventional diesel in engines. Biofuels are renewable alternatives for the large fuel demand from the global transportation sector.
- Biomass can also be anaerobically digested by microbes to generate biogas, a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide. This biogas can directly substitute for natural gas as a heating and cooking fuel. Converting landfill waste and manure to biogas captures methane emissions and provides a renewable alternative to fossil natural gas.
- On a larger scale, there are several methods to generate electricity from biomass feedstocks. Co-firing biomass with coal in existing power plants requires little new infrastructure. Dedicated biomass power facilities use direct combustion, gasification, or anaerobic digestion to produce power. The flexibility of biomass allows renewable electricity generation dispersed across rural areas.
- This range of technologies allows biomass energy to be tailored to the needs of the local community. Biomass resources can be converted into centralized electricity generation, distributed biogas systems, or biofuels for transportation. By comparison, fossil fuels like underground coal or shale gas lack this flexibility in end-use applications.
The versatility of biomass energy means it can provide sustainable power, heat, and fuel in diverse sectors from electricity to industry to transportation.
With the right technology path, locally available biomass resources can be customized to replace fossil fuel usage across the global energy economy. The multi-faceted nature of biomass feedstocks and conversion processes enhances its role as a flexible pillar of renewable energy systems.
![]()
5. Wide Availability

A major advantage of biomass energy is that it is widely available and accessible across the globe. Biomass resources are abundant on both a local and global scale, allowing localized energy generation. This contrasts with fossil fuels that are restricted to select locations.
On the local level, most regions have access to some form of biomass feedstock. Common sources include:
- Agricultural residues like corn stover, sugarcane bagasse, and rice husks from nearby farms.
- Forestry wastes such as sawdust, fallen branches, and thinnings from logging operations.
- Food wastes from restaurants, homes, and food processing plants.
- Yard clippings gathered from local maintenance of parks, gardens, and public green spaces.
- Landfill gas produced from municipal solid waste decomposing underground.
Even urban areas generate substantial biomass waste streams that can be utilized for energy production. Rural communities have even more ready access to forestry and agricultural residues for bioenergy.
When viewed on a global scale, the potential biomass resource is enormous. Studies estimate the global technical potential for biomass exceeds 500 exajoules per year, nearly 1.5 times current total energy demand. This dwarfs the supplies of finite fossil fuels. With global biomass resources widespread across agricultural lands, forests, and waste streams, most regions can source substantial local feedstock.
The localized nature of biomass offers energy self-sufficiency that is hard to achieve with concentrated fossil fuels. Oil and coal must be transported over long distances from extraction source to consumers. In contrast, distributed biomass resources allow local production of energy near the point of use. This distributed model avoids the economic and security risks of reliance on energy imports.
In summary, the high availability and accessibility of biomass feedstocks from local sources enables decentralized energy generation. This distributed approach with biomass contrasts with the geopolitical constraints around fossil fuel reserves that are concentrated in only certain parts of the world. Widely dispersed biomass supports localized energy solutions.
![]()
6. Cheap Raw Materials

Because biomass feedstock is so widely accessible, localized biomass facilities can provide major economic benefits and jobs wherever they are located. Using local biomass to produce energy supports rural communities and strengthens local economies.
- Constructing new biomass energy plants brings huge investments into rural areas. These projects create local construction and manufacturing jobs to build the plants. Once up and running, biomass power plants employ full-time workers to operate the facility and manage the biomass supply chain. For example, a 50 MW biomass power station requires $150-200 million in capital investment and employs around 40 full-time workers.
- Smaller facilities like biomass combined heat and power (CHP) plants and biogas digesters also create rural jobs. CHP plants which produce both electricity and steam/heat provide efficient decentralized power. Installing simple biogas digesters on farms produces cooking and heating fuel from organic waste. These systems are built and run by local workers.
- The operation of biomass facilities has broader impacts on rural economies. Farmers and foresters can gain stable income supplying biomass feedstock to the plants. Logistics networks emerge to harvest, collect, and transport large volumes of biomass. Suppliers are needed to provide equipment necessary for feedstock processing and delivery.
- When bioenergy replaces imported fossil fuels, energy costs are kept within the local economy rather than exported out of the region. Indirect jobs are supported across the supply chain, with local restaurants, shops, and services gaining more business from biomass facility workers.
- By using local biomass resources to meet local energy demands, bioenergy keeps economic benefits circulating within rural communities. This local job creation and revenue from biomass energy systems boosts the prosperity of rural areas.
Decentralized biomass energy promotes self-reliance and robust local economies in rural communities around the world. This local ownership contrasts with fossil fuel power’s tendency to concentrate wealth in oil, gas, and coal companies. Transitioning to sustainable bioenergy empowers rural populations.
![]()
7. Self-Sufficiency Can Be Achieved

Using biomass is an effective form of recycling waste that otherwise ends up in landfills. Agricultural residues, timber slash, crop leftovers, and even municipal solid waste can be converted into useful energy instead of taking up space in a landfill.
- For example, the husks, stalks, and straw leftover after harvesting rice, wheat, corn, and other grains are typically burned in open fields or left to decay. This agricultural residue can instead be collected and used for power generation. Rice husks, which are over 25% of the rice harvest, provide a low-cost biomass feedstock.
- Likewise, sawmill leftovers like sawdust, bark, and black liquor from the pulp and paper industry have energy value. Sawdust and pulp effluents can fuel boilers and process heat systems at sawmills and paper mills. Capturing this waste biomass is cheaper than disposing of it.
- Food processing facilities generate organic waste streams high in carbohydrates, fats, and proteins that can produce biogas through anaerobic digestion. Using food waste avoids landfill methane and provides renewable fuel. Even municipal solid waste contains up to 65% organic matter which can be converted into biogas rather than taking up landfill space.
- In addition, purpose-grown energy crops like switchgrass, poplar, and willow are perennials that require less tilling and replanting than conventional crops. Their deep root systems enhance soil health and reduce erosion. Dedicating a portion of land to perennial bioenergy crops improves the sustainability of agriculture.
Overall, the use of residues, wastes, and dedicated energy crops as biomass feedstocks supports more sustainable land management. Biomass energy production helps reduce waste disposal while improving soil conditions, water quality, and biodiversity. Converting these organic materials into renewable energy has multiple environmental benefits beyond just displacing fossil fuels.
![]()
8. Biomass As A Fertilizer

The ash residue left after burning biomass contains valuable nutrients that can offset the need for chemical fertilizers. Using bioash as a fertilizer adds nutrients back into the soil, reducing demand for synthetic fertilizers made with fossil fuel inputs.
- When biomass feedstocks are combusted to produce energy, burner ash is left over as a byproduct. This ash contains significant amounts of mineral nutrients like calcium, potassium, magnesium, and phosphorus that plants require to grow. As a result, bioash can replace some chemical fertilizers when applied to fields.
- For example, wood ash contains about 25% calcium oxide and 5-7% potassium oxide. Spreading wood ash supplements soil potassium levels which boost crop growth and provide pest resistance. Rice husk ash is rich in silica, making it useful for rice production where silica improves grain yield.
- Ash from burned crop residues like straw and stalks returns nutrients like phosphorus and potassium back to the soil. This reduces the need for importing phosphate and potash fertilizers. Closing the ash-soil loop reduces nutrient loss and enhances the sustainability of crop production systems.
- In areas with poor soils deficient in key minerals, bioash fertilization can provide missing nutrients. Magnesium and calcium are often lacking in weathered or sandy soils. Spreading ash with these minerals corrects the imbalance. Bioash also raises soil pH in acidic soils which improves microbial health and nutrient availability.
- Synthetic fertilizer production relies heavily on fossil fuels for raw materials and energy. The production of nitrogen fertilizer alone accounts for over 1% of global energy use, mostly from natural gas. Replacing a portion of chemical fertilizers with bioash reduces both fossil energy demand and carbon emissions.
Overall, reusing ash from biomass power generation boosts soil fertility, cuts fertilizer requirements, and improves agricultural sustainability. Nutrient recycling from bioash enhances soil health while avoiding carbon emissions from fertilizer manufacturing.
![]()
9. Part of the Carbon Cycle

Carbon released from burning biomass is part of the natural carbon cycle since the carbon originated from atmospheric CO2 absorbed by plants. Using biomass energy helps maintain the balance of the global carbon cycle that sustains all life.
- During photosynthesis, plants absorb CO2 from the air and convert it into carbon compounds like sugars and cellulose that make up their tissues. This carbon gets incorporated into leaves, branches, stems and roots as the plants grow. The carbon is temporarily stored within the plants.
- When biomass feedstocks are later combusted to produce energy, the same carbon is released back into the atmosphere as CO2. Since this carbon was recently above ground and circulating in the active carbon cycle, it does not disrupt the equilibrium. The balanced flows of the global carbon cycle are maintained by recycling carbon between the biosphere, atmosphere and oceans.
- In contrast, extracting and burning fossil fuels releases carbon that has been trapped underground away from the carbon cycle for millions of years. This injects new carbon from a geological reservoir into the surficial biosphere, causing an imbalance in the natural carbon flows between reservoirs.
- While biomass emits CO2 when combusted, it pulls this same amount of CO2 from the air as future biomass grows to replace the feedstock harvested. As long as biomass stocks are replenished sustainably, the net carbon cycle impact is neutral. However, burning fossil fuels has a one-way impact of pumping ancient buried carbon to the surface.
Biomass energy helps sustain the natural carbon balance that existed before digging up and burning fossil fuels. Maintaining balanced flows of carbon between the atmosphere, biosphere and soils limits the CO2 buildup causing climate change. Using renewable bioenergy aids the self-regulation of the global carbon cycle.
![]()
10. Less Transportation Cost

With biomass feedstocks widely dispersed, costs of transporting bulk biomass over long distances is minimized. Biomass energy facilities can be located close to the source of biomass, saving heavily on transportation costs.
- A key advantage of distributed biomass is that power generation facilities can be sited very close to the feedstock source. Agricultural residues like corn stover and sugarcane bagasse are readily available adjacent to croplands surrounding a bioenergy plant. Forestry slash and sawdust can fuel small power stations at the logging site. Biogas digesters are installed right on farms to convert manure and silage to methane.
- This proximity of biomass resources to the energy facility minimizes transportation miles. In many cases, the feedstock only needs to move hundreds of yards from the field to the plant, via conveyors or pipes. Short-distance transport of biomass is orders of magnitude cheaper than long-haul transport.
- In contrast, fossil fuels like oil, coal and natural gas require long-distance transport from concentrated deposits to widespread users. Coal may travel thousands of miles by train from mines to power plants. Oil pipelines stretch across continents from oil fields to refineries. Natural gas shipment requires chilled tankers and expensive liquefaction.
- These fossil fuel supply chains have massive costs and energy requirements for long-distance transportation that can exceed the energy content of the fuel itself. The localized nature of biomass energy avoids most of these transportation costs and losses.
Overall, the decentralized distribution of biomass sources allows energy generation near the point of feedstock origin, saving heavily on bulk transportation. Localized energy production from locally sourced biomass feedstocks minimizes transport costs and energy usage. This reinforces the sustainability benefits of transitioning our energy systems to renewable bioenergy.
![]()
Top 10 Biomass Energy Cons
Biomass energy has various disadvantages or cons as well. Let us review some of them below:
1. Costly Large-Scale Setups

Small biomass setups might not be that expensive, but energy extraction from biomass on a large scale requires proper machinery, decomposers, furnaces, and incubators.
- For all these facilities, a right amount of money is needed, and it is a common concept that biomass energy is not worth investing this much amount of money once combined with other demerits.
![]()
2. Requirement of Large Space

The process of treating and producing energy from biomass requires properly spaced huge containers.
This process also involves the appropriate setup of energy extraction plants from biomass that cannot be performed without the availability of huge space.
![]()
3. Global Warming Effects

Some gases like nitrous oxide, methane, and carbon dioxide may escape from containers during the production of biomass, into environment hence contributing to global warming.
- As well as biomass is not exactly a 100% pollution free source.
- Burning of biomass may yield pollution as bad as pollution produced from burning of coal or oil.
![]()
4. Slow Raw Material Production

Biomass might be a renewable source of energy. However, the production of its raw material is pretty slow.
- Biomass is produced from organic waste, dead plants, animal dung and wood, and production of all this stuff is slow as compared to the consistent supply of fossil fuels.
- Alternatively, to speed up the biomass energy production, cutting trees will be an option; hence, this will yield into deforestation.
![]()
5. Reduced Efficiency

It has been observed that biodiesels for vehicles have been proved less efficient as compared to petrol or gas.
- Bioethanol is way less effective than gasoline.
- It has been found that biodiesels somehow reduce engine efficiency as well.
![]()
6. Reduced Soil Potential

Organic material must be introduced to the soil over time to maintain its nutrient level.
- Dead or decaying matter act as natural compost and replenish soil efficiency naturally.
- However, when these matters are removed from soil to grow biomass and extract energy from it, no natural compost will be available to the ground, and hence soil potential will decrease.
- Although biomass ash can act as fertilizer, it might not be able to fulfill the nutrient requirement for such nutrient deficient soil.
![]()
7. Production of Unpleasant Odor

Biomass incineration produces a specific type of unpleasant smell which spreads quite rapidly in the surrounding area and so producing uncomfortable working conditions near the incinerator.
Many pathogens may also escape from the container.
![]()
8. Water Requirement

Large amounts of water are required for the processing and recycling of biomass. Studies of the future state of water availability and use need to include the possibility of new high demands for water from a growing bioenergy sector.
![]()
9. May Have Seasonal Production

Biomass raw material is more commonly present in warmer seasons.
- Even in northern areas of United States, biomass products are not available in winter months.
- It implies that biomass technique is more effective in areas of warmer regions. Moreover, warmer areas have more crop production as compared to cold regions.
![]()
10. Health Hazards

Biomass from animal dung leads to spreading of harmful bacteria in its vicinity hence causing many diseases.
Without proper ventilation, biomass incineration can produce lung problems.
![]()
Biomass technique can undoubtedly prove to be an advantageous and beneficial method. However, to gain full potential of the processes, all the related obstacles and hindrances are to be removed.
Biomass productions on a small scale are beneficial and should be encouraged especially in rural areas where there is no energy supply already.
![]()
Cite This Page
References
- “biomass energy | National Geographic Society”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “CHAPTER 1. RENEWABLE ENERGY OVERVIEW”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Fossil Fuel – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Will biomass be the environmentally friendly fuel of the future? – ScienceDirect”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Biomass resource facilities and biomass conversion processing for fuels and chemicals – ScienceDirect”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Biomass, Hot Issue – Smart Choices In Difficult Times”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “A review on biomass as a fuel for boilers – ScienceDirect”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Biomass and Bioenergy – ScienceDirect”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Recycling of manure nutrients: use of algal biomass from dairy manure treatment as a slow release fertilizer – ScienceDirect”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Importance of biomass in the global carbon cycle”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- em>”The relative cost of biomass energy transport | SpringerLink”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Cost optimization of biofuel production – The impact of scale, integration, transport and supply chain configurations – ScienceDirect”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Carbon Capture Vs Biomass”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “CO2 emissions from biomass combustion for bioenergy: atmospheric decay and contribution to global warming”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Current Challenges in Commercially Producing Biofuels from Lignocellulosic Biomass”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Fuel efficiency and exhaust emissions for biodiesel blends in an agricultural tractor” – By Y.X. Li, N.B. McLaughlin*, B.S. Patterson and S.D. Burtt. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Biofuels in the U.S: Challenges and Opportunities – ScienceDirect”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Journal of Environmental Quality Abstract – SPECIAL SUBMISSIONS Science of Odor as a Potential Health Issue | Digital Library”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Future Biomass Energy Supply: The Consumptive Water Use Perspective”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Seasonal and inter-annual variability in bacterial production and biomass in a temperate estuary”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.
- “Gender and health issues in the biomass energy cycle: impediments to sustainable development – ScienceDirect”. Accessed December 26, 2018. Link.