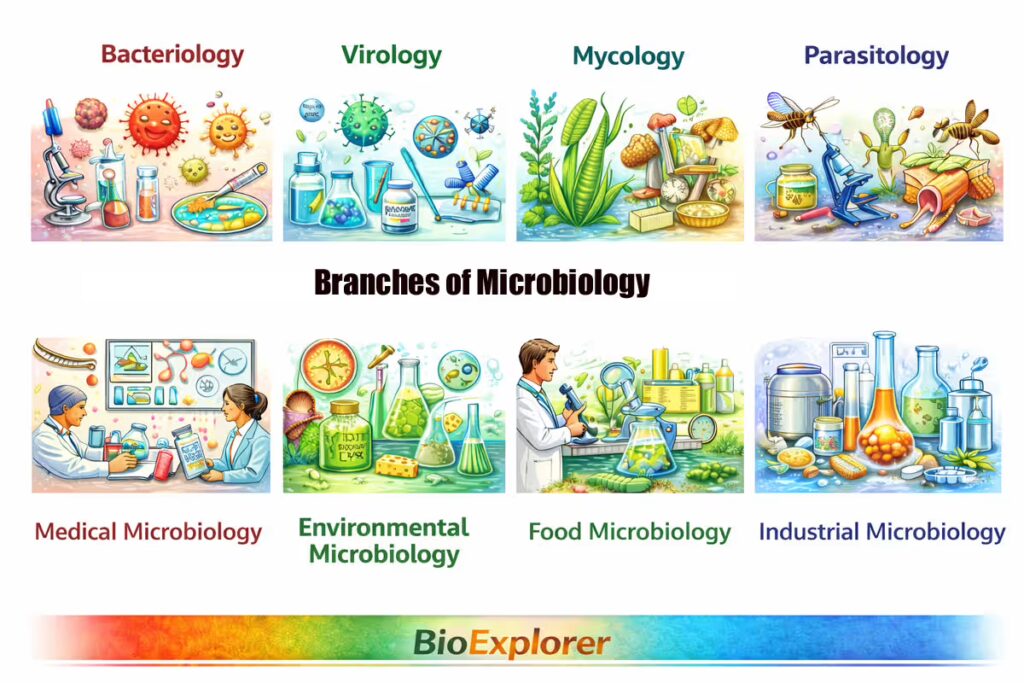
Branches of Microbiology
The term 'Microbiology' first originated from the Greek words “mikros” and “bios“, meaning small and life. It is essentially a branch of science that focuses on the study of microscopic organisms.
Jump to:
- Branches of Microbiology
- A) Taxonomic Branches
- B) Integrative & Applied Branches
- Linkage To Other Biology Branches
- Microbiology Articles
- 15 Best Microbiology Textbooks
- Latest Discoveries In Microbiology 2019
- Top 10 Microbiology News of 2020
- Top 11 Microbiology News In 2017
- Top 15 Latest Microbiology & Virology Discoveries in 2018
- Top 15 Microbiology News of 2021
- Top 15 Microbiology News of 2022
- Top 15 Online Microbiology Courses For US Students
- Resources
Usually, there are three distinct classes of Micro-Organisms. First type is a unicellular microscopic organism that contains just a single cell. The second type of micro-organism is multi-cellular and finally, the last type is known as a-cellular, meaning lack of cells. The counts of microscopic organisms or microbes on earth are huge. These microbes are only visible under a microscope. Microbiology is the study of all these micro-organisms.
Branches of Microbiology
To study the “invisible world“, scientists specialize in specific groups of microbes or specific environments where microbes live.
A) Taxonomic Branches
These branches are named after the specific type of microbe the scientist is researching.
- Bacteriology: Bacteriology is the study of bacteria—their morphology, classification, genetics, physiology, and roles in disease, industry, and ecology. This includes everything from the “good” bacteria in your gut to the “bad” ones that cause bacterial diseases. Bacteria exhibit a variety of shapes of bacteria, including cocci, bacilli, vibrio, spirilla, and spirochetes among others.
- Virology: Virology is the study of viruses—their structure, replication, infection mechanisms, evolution, and roles in disease across hosts. Scientists here look at how viruses infect cells and how to create vaccines to stop them.
- Mycology: Mycology is the study of fungi—including yeasts, molds, and mushrooms—with emphasis on their structure, growth, reproduction, and roles in health, disease, and biotechnology. This is vital for both medicine (fungal infections) and the food industry (bread and cheese). Explore the fermentation biology for more details.
- Nematology: Nematology is the sub-division of microbiology that focuses on the structure, physiology, and pathogenicity of nematodes (roundworms), particularly those that are microscopic and interact with hosts or microbes in medical, veterinary, and agricultural systems.
- Phycology: Phycology is the branch of microbiology that deals with the scientific study of algae, especially microscopic and unicellular forms, focusing on their structure, physiology, ecology, and roles in health, industry, and the environment. Algae are critical for the environment because they produce much of the world’s oxygen.
- Parasitology: Parasitology in microbiology focuses on the study of parasitic organisms—such as protozoa, helminths, and arthropods—their life cycles, mechanisms of disease, transmission, and interactions with host immunity.—organisms that live on or inside a host to survive, often causing diseases like malaria. Learn more about the top 12 diseases caused by protozoa here.
How Are Viruses Different From Bacteria?
B) Integrative & Applied Branches
These branches look at how microbes interact with the world around them or how we can use them to our advantage.
- Medical Microbiology: This is likely the most famous branch. It focuses on the microbes responsible for human disease. Medical microbiologists identify pathogens and help doctors choose the right treatment.
- Environmental Microbiology: This branch studies how microbes function in their natural habitats, like soil and water. They are the “recyclers” of the planet, breaking down dead matter and cleaning toxins out of the environment.
- Food Microbiology: These scientists study the microbes that spoil our food, as well as the ones we use to create it. If you enjoy yogurt, beer, or kimchi, you can thank food microbiologists.
- Industrial Microbiology: Similar to White Biotechnology, this branch uses microbes to create products on a massive scale, such as producing antibiotics or using yeast to create fuel.
Top 15 Current Environmental Issues in the US
Linkage To Other Biology Branches
Microbiology is the “bridge” between various branches of biology:
- Biochemistry: Microbiologists study the chemical reactions inside a bacterial cell.
- Genetics: They study how bacteria swap DNA to become “superbugs” (antibiotic resistance).
- Biotechnology: They use microbes as “factories” to build new medicines.
Suggested Reading:

History of Microbiology
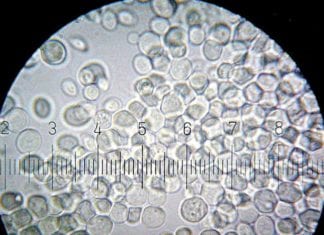
Here, it is worth mentioning that virus, although microscopic are nowadays termed as “Organisms” due to their very complex molecular pattern. Microbiology and Immunology are closely related.
Studies prove that microbes are diverse organisms that can grow and thrive in any environment, regardless of how extreme it is. From hot, volcanic springs to freezing, Antarctic deserts, from salt flats to pools of saturated brine, most microbes can survive anywhere.
Microbiology Articles

15 Best Microbiology Textbooks
Latest Discoveries In Microbiology 2019

Top 10 Microbiology News of 2020

Top 11 Microbiology News In 2017
Top 15 Latest Microbiology & Virology Discoveries in 2018

Top 15 Microbiology News of 2021

Top 15 Microbiology News of 2022

Top 15 Online Microbiology Courses For US Students
Resources
List of Bacterial Names with Standing in Nomenclature
The List of Bacterial Names with Standing in Nomenclature includes, alphabetically and chronologically, the nomenclature of bacteria and the nomenclatural changes as cited in the Approved Lists of Bacterial Names, or published, or validly published in the International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology. Link
BioMolecular Networks Initiative: Microbiology
The Biomolecular Network Initiative (BNI) is headquartered at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL). The Initiative and PNNL are coupling experience and expertise in environmental microbiology with capabilities in molecular and computational sciences to develop unique capabilities for investigating the function and structure of biological macromolecules, microbial cells, mixed populations of microbial cells, and microbial communities. Link
Department of Bacteriology (University of Wisconsin-Madison)
Welcome to the Bacteriology Department. This site contains information about microbiology for scientists, students and anyone interested in microbiology. Link
Department of Microbiology & Immunology
Department of Microbiology & Immunology at the University of Leicester. Link
Department of Microbiology at Monash University
The main research and academic interests of the Department of Microbiology are medical microbiology and microbial pathogenesis, infection and immunity, vaccine development, molecular parasitology, molecular virology, viral gene expression, molecular microbiology, and microbial genetics, biotechnology. Link
Department of Molecular Biosciences – Section of Microbiology
The discipline of Microbiology at the University of Kansas has a long tradition of research excellence in the many sub-disciplines within microbiology: Immunology; Microbial Genetics; Pathogenic Microbiology; Physiology; and, Virology. Link
DOE Microbial Genome Program
The focus of the Microbial Genome Program is to develop the ability to sequence the genetic material of microbial organisms. This will provide detailed genetic information on microorganisms with importance to the environment, energy production, and other important applications. The program, spun-off from the Human Genome Program in 1994, is already providing complete sequence information on key microorganisms. Link
Enhanced Microbial Genomes Library
The Pole Bio-Informatique Lyonnais (PBIL) presents the Enhanced Microbial Genomes Library (EMGLib), a database devoted to the completely sequenced bacterial genomes and the yeast genome. Users may search the database by keyword, sequence name, or accession number. PBIL includes associated documents and links to sites related to microbial genomes. Link
Extremophile Molecular Microbiology Research Group
The EMMRG is led by Dr Stephen Cummings: it utilises molecular techniques to investigate the adaptations of extremophilic bacteria. Link
Hardy Diagnostics: Microbiology Glossary
One of the largest collection of microbiology terms and abbreviations. Link
Humboldt University Microbiology
Research Topics: The proteobacterium Alcaligenes eutrophus serves as a model organism for the investigation of two alternative pathways of bacterial energy conservation: the oxidation of molecular hydrogen and denitrification. Both pathways involve complex biosyntheses of cofactor-containing oxidoreductases, membrane transport processes and transcriptional regulation. Link
Introduction to Bacterial Structure
A great site containing great information and images of bacterial structures. If you are wanting an introduction to how bacteria are put together this is a great starting place. Link
Introduction To Clinical Microbiology
This site contains a large number of excellent images of bacteria, culture media, and biochemical tests. Link
Microbes in Norwich
This site was created to bring together the wide variety of microbiological research being undertaken on the Norwich Research Park near the city of Norwich, England. Link
Microbial Genetics: PLP 428 Home Page
Class notes & links from University of Arizona. Link
Stanford Center for Tuberculosis Research
The purpose of these pages is to foster international collaborations between tuberculosis researchers. We hope that our new layout helps you learn more about what we do here at Stanford, and about tuberculosis research in general. There are links to home pages of personnel, including those of the Principle Investigator here, Dr.Peter Small. A summary of research and a list of publications for the Stanford Center for Tuberculosis Research are provided. Link
The Microbiology Information Portal
A microbiology information portal containing a vast collection of resources including articles, news, frequently asked questions, and links pertaining to the field of microbiology. Link
Cite this page
Bio Explorer. (2026, January 27). Branches of Microbiology. https://www.bioexplorer.net/divisions_of_biology/microbiology/
