
Elephant Evolution: Elephants evolved over a period of millions of years. It took 60 million years for elephants to evolve their long tusks and trunks. The earliest ancestors of elephants looked nothing like elephants.
As time went by, the bodies of the animals became larger, the trunks of the animals became longer, and the teeth of the animals turned into tusks.
Let’s explore the ancestors of elephants starting from the earliest in more detail below:
Table of Contents
Elephant Evolution
Moeritherium
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Meaning | Moeris beast |
| Time of Discovery | Early 1900s |
| Named By | Charles Williams Andrews |
| Year of Naming | 1901 |
| Place Lived | North America |
| Time Lived | 37-35 million years ago |
| Period Lived | Eocene Period |
| Weight | About 90 kg |
| Length | About 2.4 m |
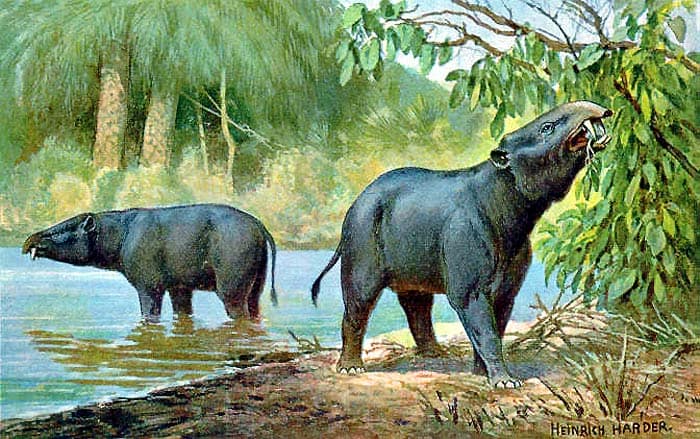
Moeritherium is a genus of animals that are ancestors of elephants. Moeritherium was named after Lake Moeris combined with Ancient Greek.
- Animals in this genus were proboscideans meaning it was of the order Proboscidea. Their upper lip was very long (it might have been used to hold plants).
- Moeritherium animals were also related to manatees (also known as sea cows). Moeritherium animals had sturdy legs. The teeth of Moeritherium animals looked like small tusks, but they looked more like the teeth of a hippo.
- Based on studies of their skulls, scientists think these animals did not have a trunk. They had strong legs and a short tail. These animals were as long as a horse, and as heavy as a boar.
- They are in fact closely related to hippos than elephants. These animals had many traits similar to that of hippos. Moeritherium animals are technically pachyderms.
![]()
Deinotherium
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Meaning | Terrible Beast |
| Time of Discovery | Early 1800s |
| Named By | Johann Jakob Kaup |
| Year of Naming | 1829 |
| Place Lived | What is now Africa, Asia, and Europe |
| Time Lived | 10 million years ago to 10,000 years ago |
| Period Lived | Miocene-Modern Period |
| Weight | About 10886 kg |
| Length | About 6 m |
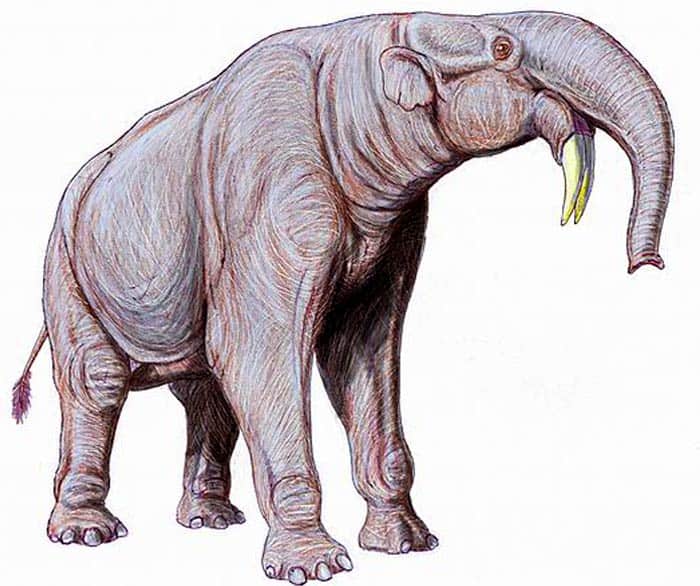
Deinotherium is a genus of animals that are ancestors of elephants that resemble elephant more than animals of the genus Moeritherium.
- The word Deinotherium was derived from the Ancient Greek language.
- These animals originated from Europe, but they then traveled to different continents like Asia.
- Animals in this genus had a very short trunk. Animals in Deinotherium had tusks as well, but unlike modern-day elephants, animals in this genus had their tusks in their lower jaw meaning the tusks pointed downwards instead of upwards like elephants today.
- These animals were longer than Asian elephants. The reason why these animals went extinct was because of climate change and human interference (hunting).
![]()
Gomphotherium
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Meaning | Welded Beast |
| Time of Discovery | Early 1800s |
| Named By | Hermann Burmeister |
| Year of Naming | 1837 |
| Place Lived | What is now North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa |
| Time Lived | 15-10 million years ago |
| Period Lived | Miocene-Pliocene Period |
| Weight | About 4535 kg |
| Length | 3.9 m |
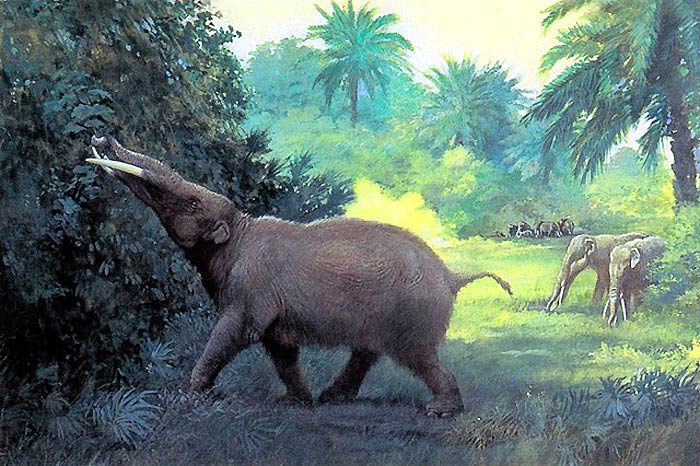
Unlike modern elephants, animals in the genus Gomphotherium had two sets of tusks – one coming from their upper jaw and one from the lower jaw.
- The lower tusks were used to shovel up plant matter from lakes that were flooded.
- Gomphotherium animals lived during the Miocene period and Pliocene period.
- Believe it or not, animals in the genus of Gomphotherium were about two times the length of a king-size bed.
- Also they were lighter than modern-day elephants. Gomphotherium animals were about 3 meters tall.
![]()
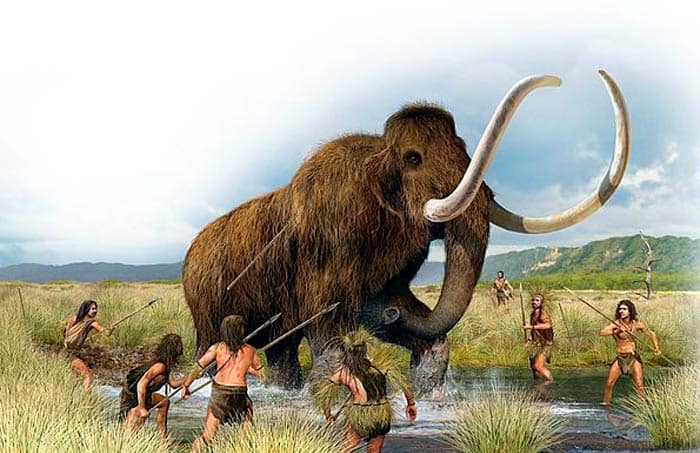
Woolly Mammoth

| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Meaning | No meaning |
| Time of Discovery | Late 1700s |
| Named By | Joshua Brookes |
| Year of Naming | 1828 |
| Place Lived | What is now North America, Europe, Asia |
| Time Lived | 5 million years ago – 4500 thousand years ago |
| Period Lived | Pliocene-Holocene Period |
| Weight | About 5433 kg |
| Length | 6 m |
The woolly mammoth is the most commonly known elephant ancestor. Wooly mammoths only went extinct thousands of years ago, unlike the first three ancestors.
- Just like African elephants, woolly mammoths had two fingers on their trunks. Woolly mammoths would have been almost the same size as an elephant today.
- Early humans hunted woolly mammoths for their ivory as well as meat. Unlike modern-day elephants, woolly mammoths were covered completely with hair.
- The habitat of a woolly mammoth is called a mammoth steppe or tundra steppe. Scientists have tried to recreate woolly mammoths using DNA found, but so far, it is not working.
![]()
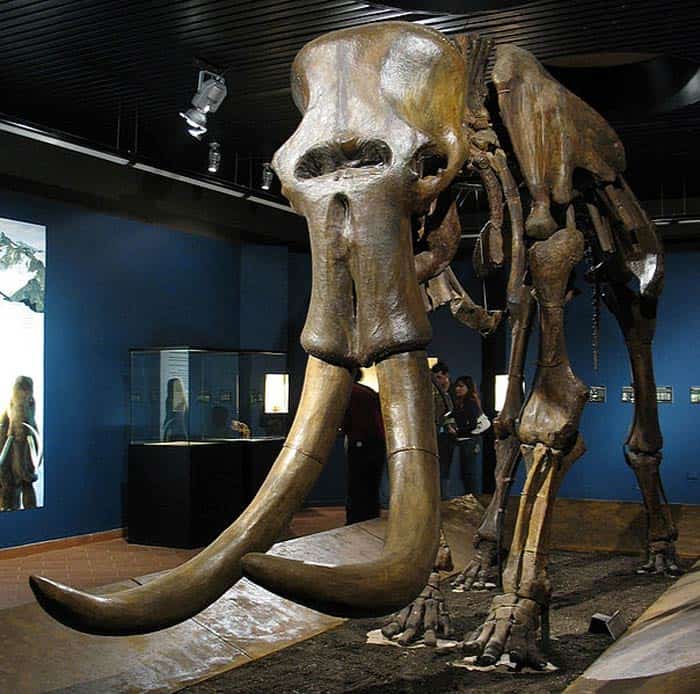
Steppe Mammoth

| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Meaning | No meaning |
| Time of Discovery | Unknown |
| Named By | Unknown |
| Year of Naming | N/A |
| Place Lived | What is now Europe and Asia |
| Time Lived | 600,000-370,000 thousand years ago |
| Period Lived | Pleistocene Period |
| Weight | About 19958 kg |
| Length | 7 m |
The steppe mammoth was two times the size of a modern elephant.
- One difference between woolly mammoths and steppe mammoths is that steppe mammoths are not covered with hair like woolly mammoths.
- The full skeleton of this humongous animal is still yet to be found.
- This mammoth’s tusks could grow as long as 4.9 meters.
- The most complete skeleton of a steppe mammoth was found in 1996.
![]()
We have seen that cells are of paramount importance to life, without which life is unsustainable. The cell theory describes the basic principles which surround and govern all cells of all living organisms irrespective of their internal features and differences, and this theory forms the basis and foundation of modern cell biology.
![]()
Cite This Page
References
- “Caroli Illigeri D. Acad. Reg. Scient. Berolinens. et Bavaricae Sod. Museo Zoologico Berolin. praefecti professoris extraord. Prodromus systematis mammalium et avium : additis terminis zoographicis utriusque classis, eorumque versione germanica : Illiger, Johann Karl Wilhelm, 1775-1813 : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive”. Accessed April 21, 2018. Link.
- “Shoulder height, body mass, and shape of proboscideans” by ASIER LARRAMENDI Accessed April 21, 2018. Link.
- “Deinotheres for lunch? A sabertooth’s tough-skinned diet | chasing sabretooths”. Accessed April 21, 2018. Link.
- “Early Pleistocene large-mammal fauna associated with…”. Accessed April 21, 2018. Link.
- “Mammuthus trogontherii (Steppe mammoth)”. Accessed April 21, 2018. Link.
- “Spear marks on mammoths carcass suggests humans were in Siberia 26k years ago | Daily Mail Online”. Accessed April 21, 2018. Link.
- “Mammuthus (Woolly Mammoth) – Facts and Pictures”. Accessed April 21, 2018. Link.











