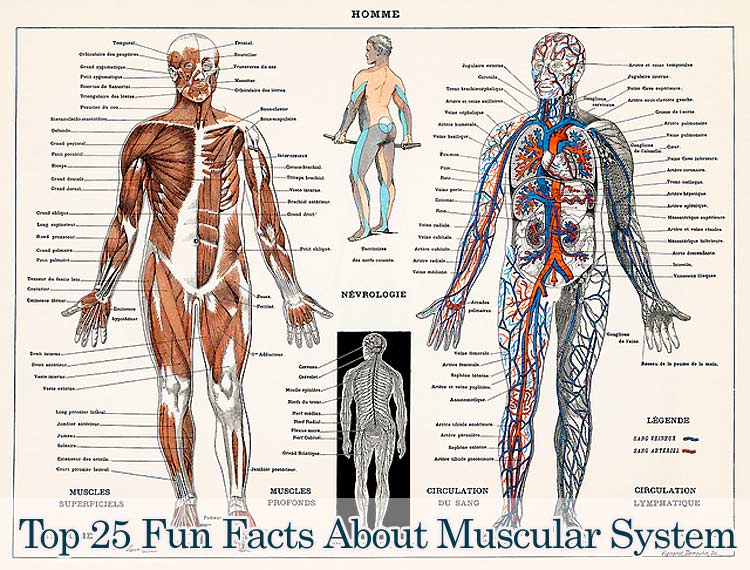
Top 25 Fun Facts About The Muscular System
The muscular system works alongside the skeletal system to keep the body aligned and completely functional. Here are the top 25 fun muscular system facts.
Fun Facts About The Muscular System: The human body comprises different systems interconnected with each other to serve the purpose of fulfilling all the essential functions of the body to sustain life. The muscular system is one such system that governs the functioning of all other organ systems.
The other organ systems are all innervated with muscles that help carry out daily functions. Muscles help the body move and are also responsible for creating facial expressions as we know them.
Apart from movements, the muscular system also works alongside the skeletal system to keep the body aligned and in the correct posture and also provides support.
Besides these, there are some interesting 25 fun facts about the muscular system.
Jump to:
- 1. 3 Major Muscle Types
- 2. Smile vs. Frown
- 3. Striated vs. Non-Striated Muscles
- 4. 600 Muscles
- 5. Muscles are 40% of the body weight
- 6. Largest Muscle - Gluteus Maximus
- 7. Smallest Muscle - Tensor Tympani
- 8. Strongest Muscle is in the jaw
- 9. Tendons help connecting muscles
- 10. Long-running Muscle - Heart Muscle
- 11. Muscle releases heat energy
- 12. Busiest Muscles - Eye Muscles
- 13. Muscles always Pull
- 14. Eyes move with the help of 6 muscle types.
- 15. Longest Muscle - Sartorius
- 16. Muscles induce Hypnic jerks
- 17. Creatine helps in Muscle Mass
- 18. Muscles help in digestion
- 19. Respiration occurs using muscles
- 20. Smooth Muscle cells help in uterus
- 21. Muscles help in blood pumping 24/7
- 22. Muscles support the body posture
- 23. Muscles can be voluntary or involuntary
- 24. Muscular dystrophy is a disorder
- 25. Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder
Top 25 Muscular System Facts
1. 3 Major Muscle Types
 At the high level, muscles of the human body are of three different types: skeletal, cardiac and smooth.
At the high level, muscles of the human body are of three different types: skeletal, cardiac and smooth.
- Skeletal muscles are attached to the bones and cartilage and help in movement and posture and support the human body.
- Cardiac muscles are found in the heart and are responsible for the heart’s pumping action.
- Smooth muscles are usually found lining the inside of different organs such as the liver, pancreas, and stomach and contain glands and cells that secrete different digestive juices. They are also present in other organ systems such as the respiratory system and the reproductive system.
![]()
2. Smile vs. Frown
 According to the studies, it takes 17 muscles to act together to bring out the smile on the face; whereas we need about 43 muscles to show a grim face. So being a positive or happy person uses less muscle energy!
According to the studies, it takes 17 muscles to act together to bring out the smile on the face; whereas we need about 43 muscles to show a grim face. So being a positive or happy person uses less muscle energy!
![]()
3. Striated vs. Non-Striated Muscles
 Muscles are made up of muscle cells that can be either striated or non-striated. They are in bundles or fibers.
Muscles are made up of muscle cells that can be either striated or non-striated. They are in bundles or fibers.
- The histological appearance of muscles resembles that of fibers or bundles.
- Muscle cells are alternating or non-alternating bands of actin and myosin, which are special muscle pigments that help in the contraction and relaxation of the muscle fibers.
- The muscle cells can elongate or shorten, which brings about the contraction and relaxation of muscle fibers that help it to perform various functions.
![]()
4. 600 Muscles
 The human body has about 600 muscles in various parts of the body.
The human body has about 600 muscles in various parts of the body.
- There are hundreds of muscles present in the human body that perform a variety of functions ranging from motion to support and aiding in digestion and other organ systems.
- In comparison, the human body has 206 bones.
- Many of these 600 muscles attach to bones and support the overall skeletal structure.
![]()
5. Muscles are 40% of the body weight

- The muscular system estimates about 40% of the total body mass. Distribution-wise, muscle cells occupy 75% of the body cells.
- Approximately 1/4th of the total body protein synthesis takes place in the muscular system.
- The total body mass and strength decrease as we age. As a result, we become weak in the old age.
![]()
6. Largest Muscle – Gluteus Maximus
 The largest muscle of the body is located in the hip and buttocks and is called gluteus maximus.
The largest muscle of the body is located in the hip and buttocks and is called gluteus maximus.
- This muscle is located in the hip region and supports the trunk and upper body.
- It is also the primary muscle involved when climbing stairs.
![]()
7. Smallest Muscle – Tensor Tympani
 The smallest muscles of the human body are present in the inner ear.
The smallest muscles of the human body are present in the inner ear.
- Tensor Tympani and Stapedius are two muscles present in the inner ear that connect to the eardrum.
- These muscles also help to connect the eardrum to the inner ear.
- In addition to the smallest muscles, the inner ear also houses the smallest bones of the body, namely the Incus, Malleus, and Stapes.
![]()
8. Strongest Muscle is in the jaw
 One of the strongest muscles of the body is in the jaw.
One of the strongest muscles of the body is in the jaw.
- Four muscles found in the jaw are responsible for chewing movements and mastication.
- These are known as the Temporalis (temporal), Masseter, Internal & External Pterygoid, and the Digastric muscles.
- The masseter muscle also helps open and close the jaw and can apply a force of around 200 pounds.
![]()
9. Tendons help connecting muscles
 Tendons connect muscles to the bones in the human body.
Tendons connect muscles to the bones in the human body.
- Tendons are connective tissue that connects muscles to the bones in the body.
- They have also attached muscles to the eyeballs.
![]()
10. Long-running Muscle – Heart Muscle
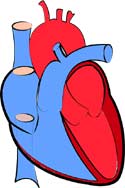 The muscle that works continuously in the body is the heart muscle.
The muscle that works continuously in the body is the heart muscle.
- Heart muscle, also known as the cardiac muscle, is striated muscle fibers that continuously work to create the pumping effect of the heart.
- They help pump about 2500 gallons of blood each day.
- The contraction of these muscles is involuntary by nature, which means they are not under the conscious control of a human being.
![]()
11. Muscle releases heat energy
 The process of muscle contraction releases a lot of heat energy.
The process of muscle contraction releases a lot of heat energy.
- Muscles contract and relax during movement. The process of contraction leads to the production of heat energy.
- When a lot of heat energy is produced, the blood vessels innervating the muscles help this energy to be redirected to the skin and prevent overheating of the muscles.
![]()
12. Busiest Muscles – Eye Muscles
 The busiest muscle in the humans is the eye muscles. The eyes have to move continuously with the help of extraocular muscles to keep a sharp vision, focus, and clear vision. The other busy muscles are cardiac muscles (for pumping blood) and diaphragm muscles (respiration), as they work nonstop to keep the person alive.
The busiest muscle in the humans is the eye muscles. The eyes have to move continuously with the help of extraocular muscles to keep a sharp vision, focus, and clear vision. The other busy muscles are cardiac muscles (for pumping blood) and diaphragm muscles (respiration), as they work nonstop to keep the person alive.
![]()
13. Muscles always Pull
 The motion provided by the muscles comprises only of the “pulling” motion and not the “pushing” motion.
The motion provided by the muscles comprises only of the “pulling” motion and not the “pushing” motion.
- Muscles are designed to pull by the process of contraction and relaxation.
- The pulling motion of some muscles in the arm helps us to push doors or other objects.
![]()
14. Eyes move with the help of 6 muscle types.
 The movements of the eye are a result of the coordinated action of six types of muscles namely superior rectus, inferior rectus, superior oblique, inferior oblique, lateral rectus, and medial rectus.
The movements of the eye are a result of the coordinated action of six types of muscles namely superior rectus, inferior rectus, superior oblique, inferior oblique, lateral rectus, and medial rectus.
- The muscles that control eye movements are known as the extraocular muscles.
- The extraocular muscles are innervated by nerves which help in control and coordination.
![]()
15. Longest Muscle – Sartorius
 The longest muscle in the body is the sartorius muscle.
The longest muscle in the body is the sartorius muscle.
- The sartorius muscle is found running down the inner side of the thigh.
- The sartorius muscle is innervated by the femoral nerve.
- It is a synergist muscle moving the hip and knee joints.
![]()
16. Muscles induce Hypnic jerks
 Hypnic jerks occur when a person is about to fall asleep, are induced by muscles.
Hypnic jerks occur when a person is about to fall asleep, are induced by muscles.
- A hypnic jerk, also known as a hypnogogic jerk is an involuntary movement that occurs during sleep.
- At times, these jerks may cause the person to awaken suddenly from their sleep.
![]()
17. Creatine helps in Muscle Mass
 Creatine is a supplement that is used widely by athletes to increase their muscle mass.
Creatine is a supplement that is used widely by athletes to increase their muscle mass.
- It is a chemical naturally found in the muscles and the brain and nutritional sources such as red meat and seafood.
![]()
18. Muscles help in digestion
 The Muscular system aids in the digestive process.
The Muscular system aids in the digestive process.
- Smooth muscles are found lining the esophagus. The contraction of these muscles helps move food down the esophagus in a wave-like motion.
- Muscles in the stomach contract and help the food move through the stomach and the duodenum.
- The muscles of the jaw help in chewing and mastication of the food to enable the swallowing process.
![]()
19. Respiration occurs using muscles
 The whole process of Respiration is aided by the muscular system.
The whole process of Respiration is aided by the muscular system.
- The muscles present in the rib cage are known as the intercostal muscles.
- Apart from these, muscles support the thoracic and abdominal cavities.
- The contraction and relaxation of these muscles aid in the expansion and relaxation of the lungs in breathing and respiration.
![]()
20. Smooth Muscle cells help in uterus
 Smooth muscle cells help in the contractile activity of the uterus.
Smooth muscle cells help in the contractile activity of the uterus.
- Smooth muscle cells are present in the myometrium of the uterus.
- They respond to steroid hormones, also known as sex hormones, that are secreted by the ovaries.
- The uterine muscles contract during the menstrual cycle, labor, and childbirth.
![]()
21. Muscles help in blood pumping 24/7
 Muscles present in the heart are responsible for its pumping.
Muscles present in the heart are responsible for its pumping.
- One of the most critical functions of muscles is the pumping action of the cardiac muscles.
- The muscles of the heart are called cardiac muscles and are present as part of the myocardium, which covers the heart.
- The contraction and relaxation of these muscles produce the pumping action of the heart, which pumps over 2500 gallons of blood through the body.
![]()
22. Muscles support the body posture
 The muscular system provides for overall stability and posture.
The muscular system provides for overall stability and posture.
- Some of the biggest and strongest muscles are in the back attached to the spine.
- They provide flexibility and stability to the body and help keep it upright.
- There are two kinds of muscle groups in the spine – local and global.
- The coordinated action of these muscle groups helps in the body’s movement and stability.
![]()
23. Muscles can be voluntary or involuntary
 There are two kinds of muscles – voluntary and involuntary. Some muscles are voluntary, which means we can control them, whereas others are involuntary and cannot be controlled.
There are two kinds of muscles – voluntary and involuntary. Some muscles are voluntary, which means we can control them, whereas others are involuntary and cannot be controlled.
- Example of the former type would be the muscles of our arms, and an example of the latter would be the cardiac muscles responsible for heart pumping and the muscles that control breathing movements.
- The voluntary muscles, such as the skeletal muscles, are under the control of the human conscious.
- Involuntary muscles are not controlled by the human being, such as the GI and cardiac muscles.
![]()
24. Muscular dystrophy is a disorder
 Muscular dystrophy is a disorder of the muscular system.
Muscular dystrophy is a disorder of the muscular system.
- It causes progressive weakness of the muscles and eventual loss of function.
- A type of muscular dystrophy known as Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a genetically inherited disorder that is more common in males than females.
- Abnormal genes cause the production of abnormal muscle proteins that leads to loss of muscle mass and ultimately, degeneration.
![]()
25. Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder
 Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder of the muscular system.
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder of the muscular system.
- This disorder causes the body’s immune cells to identify muscle cells as foreign and attack them.
- The affected muscle group is the skeletal muscle.
- Myasthenia gravis causes muscle weakness and leads to impairment of movement, as well as breathing.
![]()
Cite this page
Bio Explorer. (2026, January 28). Top 25 Fun Facts About The Muscular System. https://www.bioexplorer.net/top-muscular-system-facts.html/