Lar Gibbon

| Kingdom | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animalia | Primates | Hylobatidae | Hylobates | Hylobates lar |
Lar Gibbon Distribution
Countries
Indonesia
Laos
Malaysia
Myanmar
Thailand
Lar Gibbon Characteristics
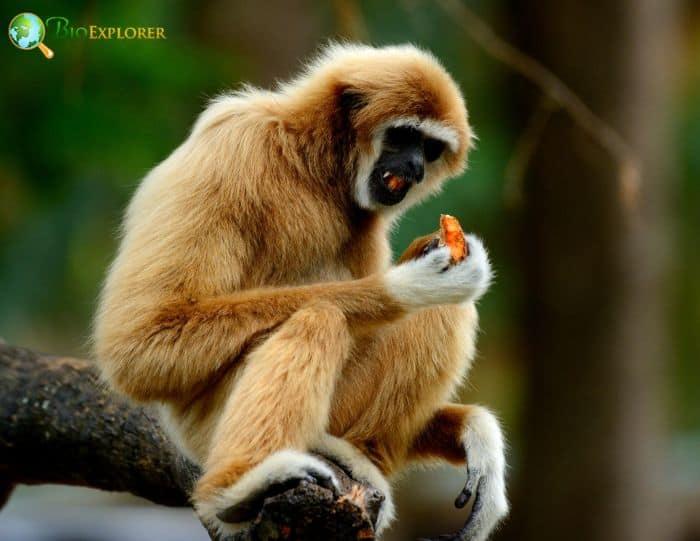

The lar gibbon[1] (Hylobates lar), also called the white-handed gibbon, is another endangered mammal in the gibbon family, Hylobatidae.
- It is among the best-known gibbons and is occasionally kept in captivity. Lar gibbons have a two-tone coat.
- They sport a dark coat that ranges from gray to black to tan or a light coat from light cream to tan.
- The bare face is encircled by a very short white or light-colored fur ring, and the hands and feet are white.
- Their elongated forelimbs, feet, and hands are used in their unique brachiation adaptations, which is their primary mode of locomotion through the treetops.
- Lar gibbons do not have a tail. Male species measure 43.5 to 58.4 cm, and female species 42 to 58 cm. Males weigh from 5 to 7.6 kg and females from 4.4 to 6.8 kg.
What Do Lar Gibbons Eat?
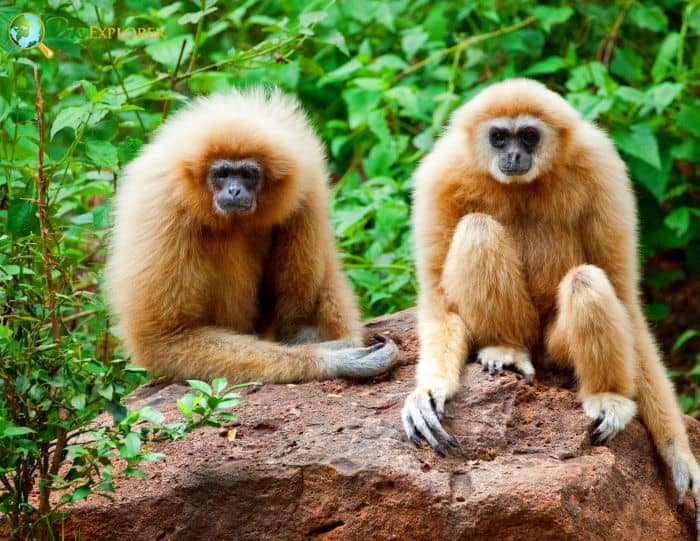

Being omnivorous, the Lar Gibbon consumes these plant sources[¶]:
- Weeping Fig (Ficus benjamina).
- Council Tree (Ficus altissima).
- Monkey Jack (Artocarpus rigidus).
- Pulasan (Nephelium lappaceum)
- Clustertree (Ficus racemosa)
- Oriental Trema (Trema orientalis).
- Cowa Fruit (Garcinia cowa).
- Myrobalan (Terminalia bellirica)
- Javanese Treebine (Cissus nodosa).
- Brown-Woolly Fig (Ficus drupacea).
- Argus Pheasant Tree (Dracontomelon dao).
- Fig (Ficus)
- Ilang-Ilang (Cananga odorata)
- Bishopwood (Bischofia javanica)
- Jacareuba (Calophyllum brasiliense)
- Langsat (Lansium domesticum)
Lar Gibbon Facts

- Home territories are defended in encounters between groups and areas where domains overlap.
- Lar gibbons use vocalization for intra-specific communication. Normal duets are based on territoriality, signaling nearby groups that pose a threat.
- These gibbons are auto- and allo-grooming animals. On average, they spend 10 hours per day allo-grooming.
- Lar gibbons communicate with conceptual songs, which are combinations of solos and/or duets performed by closely related pairs.
- Although this species is very mobile, it does not gain security during this fixed period as it may fall asleep and not wake up until a predator is upon them.

Suggested Reading: All Apes
Cite this page
Bio Explorer. (2026, January 28). Lar Gibbon. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/apes/lar-gibbon/