Golden Lion Tamarin

| Kingdom | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animalia | Primates | Callitrichidae | Leontopithecus | Leontopithecus rosalia |

- Common Name: Golden Lion Tamarin
- Taxonomy Classification Year: 1766
- Monkey Size: 20 to 36.6 cm long (8 to 13in)
- Skin Color(s): Bright orange
- Habitat: Rainforest
- Diet: Omnivorous
- Native Countries: Brazil
Golden Lion Tamarin Distribution
Countries
Brazil
Golden Lion Tamarin Characteristics
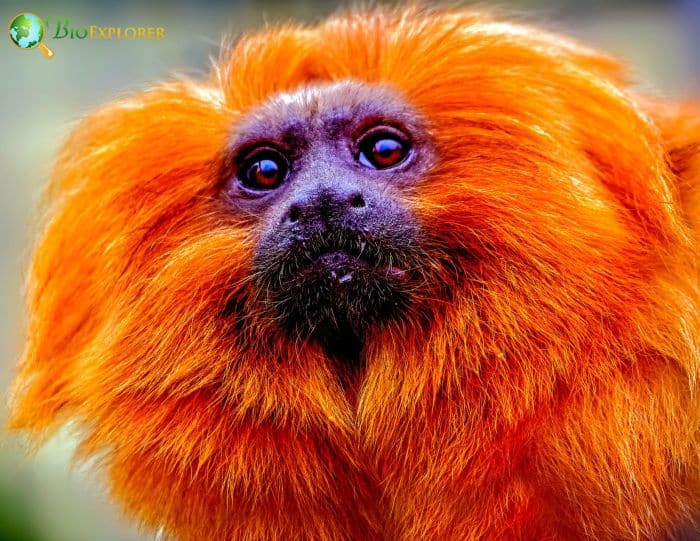

The golden lion tamarin[1] (Leontopithecus rosalia), also called the golden tamarin, is a small New World primate in the Callitrichidae family.
- They have small round heads adorned with a thick golden mane on the crown, cheeks, ears, throat, and shoulders.
- Their hairless faces are flat with widely spaced nostrils. Their bodies are draped in long, soft, silky fur ranging in color from pale gold to rich red gold.
- An interesting feature is that these monkeys have claws, not flattened nails.
- The golden lion tamarin is 200 to 366 mm (8 to 13 in) long with a tail length of 315 to 400 mm (12 to 15 in).
- There is no sexual dimorphism in Golden lion tamarins.
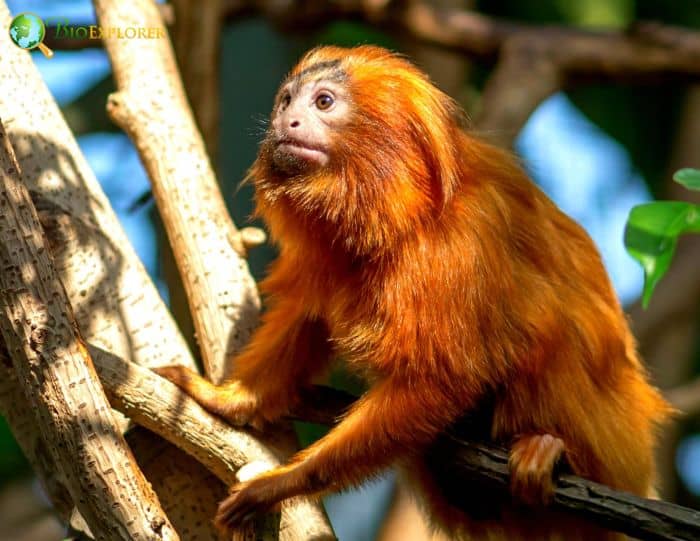

What Do Golden Lion Tamarins Eat?

Being omnivorous, the Golden Lion Tamarin diet includes but not limited to[¶]:
- Ambay Pumpwood (Cecropia pachystachya).
- Pois Doux (Inga thibaudiana).
- Icecream bean (Inga edulis).
- Johnny berry (miconia)
- Wild Balata (Micropholis guyanensis).
- Forest Snakevine (Hyperbaena domingensis).
- Punchberry (Myrcia splendens)
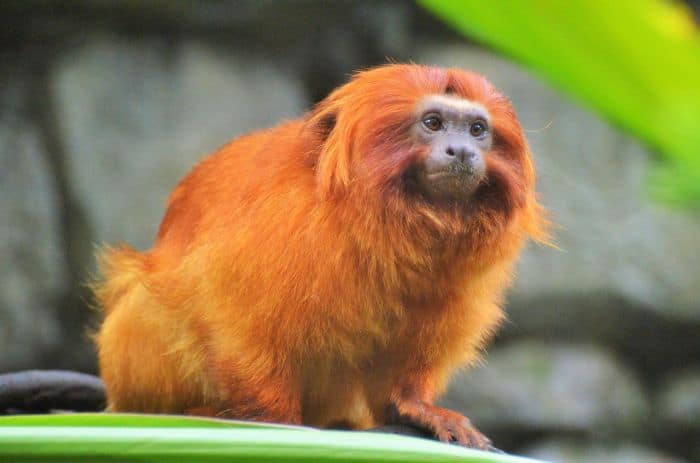
Golden Lion Tamarin Facts

- The golden lion tamarin derives its name from its vivid reddish-orange coat and extra-long hair around its face and ears, giving it a distinctive mane.
- Like most New World Monkeys, the golden lion tamarin has tegulae, claw-like nails, rather than the flat nails or ungulate found in other primates, including humans.
- By moving their sleeping nests around frequently, groups reduce the scent they leave behind and minimize the chances of predators finding them.
- Groups of these tamarin species use hollow tree cavities, thick tendrils, or epiphytes as roosting places.
- The golden lion tamarin tends to be active earlier during the hotter and wetter seasons and retire later as the days are longer.
Suggested Reading: All Types of Monkeys
Cite this page
Bio Explorer. (2026, January 28). Golden Lion Tamarin. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/golden-lion-tamarin/
