Bonobo

| Kingdom | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animalia | Primates | Hominidae | Pan | Pan paniscus |

- Common Name: Bonobo
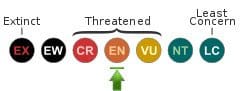
- Taxonomy Classification Year: 1929
- Monkey Size: 104 to 124 cm (40.94 to 48.82 in)
- Skin Color(s): Black
- Habitat: Forest, rainforest
- Diet: Herbivorous
- Native Countries: Democratic Republic of Congo
Bonobo Distribution
Countries
Democratic Republic of Congo
Bonobo Characteristics
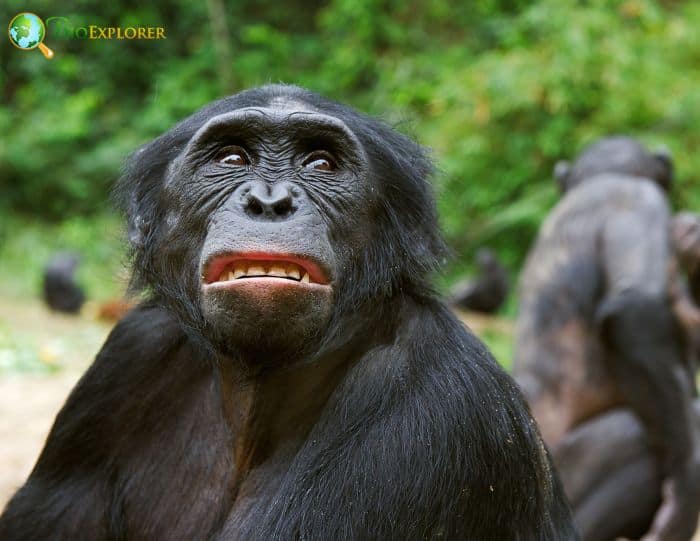

The bonobo[1] (Pan paniscus) is a great ape in danger of extinction. It is one of two species that make up the Pan genus, the other being Pan troglodytes – the common chimpanzee.
- The bonobo is generally considered more elegant than the common chimpanzee.
- Although large male chimpanzees may exceed any bonobo in mass and weight, the two species overlap significantly in body size.
- The head of the bonobo is relatively smaller than that of the common chimpanzee, with less prominent brow ridges over the eyes.
- The species has a black face with pink lips, large nostrils, small ears, and long hair on the head that forms a part.
- Females have slightly more prominent breasts, unlike the flat breasts of other female apes. However, they are not as prominent as those of humans.
- The bonobo also has a slender torso, narrow shoulders, a slender neck, and long legs compared to the common chimpanzee.

What Do Bonobos Eat?
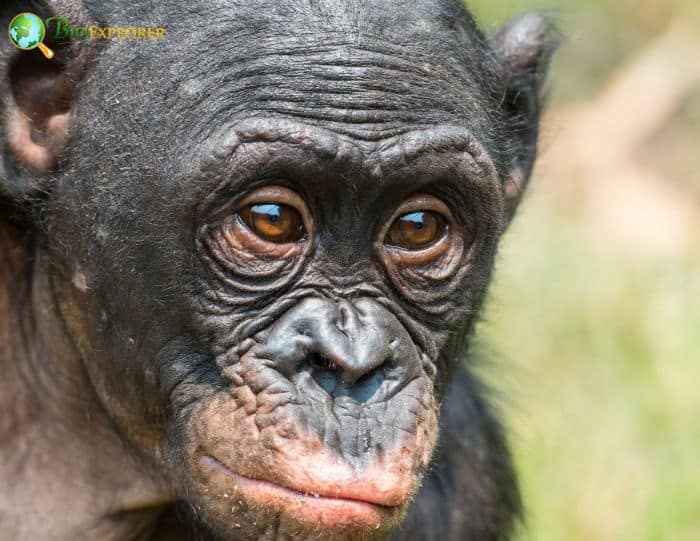

The Bonobo consumes these organic matter namely[¶]:
- Antrocaryon (Antrocaryon micraster)
- African Breadfruit (Treculia africana).
- Ragleaf (Crassocephalum)
- Treebind (Cissus)
- Umbrella Tree (Musanga cecropioides).
- Persimmons (Diospyros)
- Goldenleaf (Chrysophyllum)
- Aframomum (Aframomum)
- Tail Grape (Artabotrys)
- African Nutmeg (Pycnanthus angolensis).
- African Mammee-Apple (Mammea africana).
- Boleko Nut (Ongokea gore).
- Boarwood (Symphonia globulifera)
- Emien (Alstonia boonei)
- Eben Tree (Dacryodes edulis).
- Umbrella-Tree (Maesopsis)
- Tallow Tree (Allanblackia floribunda).
- Fig (Ficus)
- Devil’s-Pepper (Rauvolfia)
Bonobo Facts
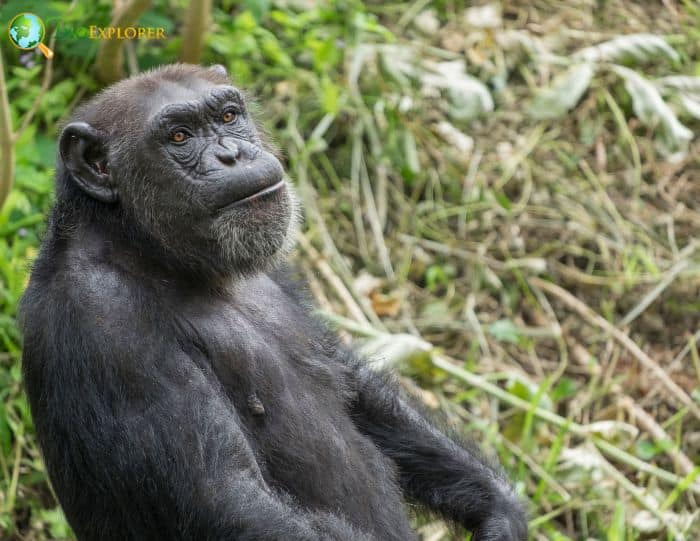

- Bonobos are both arboreal and terrestrial. Most floor movements are characterized by knuckle quadrupedal walking.
- Multivariate analysis has revealed that bonobos are more neothenized than the common chimpanzee, taking into account traits such as the relatively long torso.
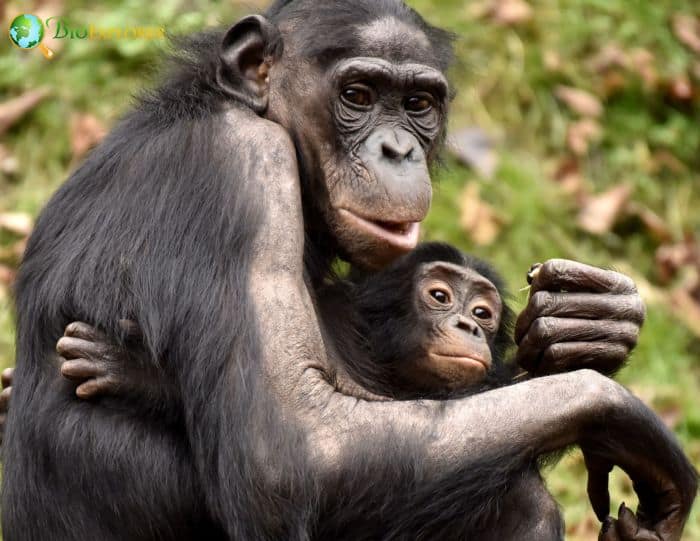
- The bonobo, like humans, has highly individualized facial features such that one individual can be clearly distinguished from another, a trait that lends itself to the visual recognition of faces in social interactions.
- Males form long-lasting friendships with females, and female bonobos, in turn, prefer to associate and mate with males who are respectful and easygoing toward them.
- Due to the nomadic nature of females and the food evenly distributed in their environment, males do not gain an obvious advantage when forming alliances with other males or defending a range like chimpanzees.
Suggested Reading: Types of Apes
Cite this page
Bio Explorer. (2026, January 28). Bonobo. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/apes/bonobo/
