Tibetan Macaque

| Kingdom | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animalia | Primates | Cercopithecidae | Macaca | Macaca thibetana |

- Common Names: Tibetan Macaque, Milne-Edwards’s Macaque, Chinese stump-tailed Macaque
- Taxonomy Classification Year: 1870
- Monkey Size: 49 to 71 cm (19 to 28 in)
- Skin Color(s): Gray to brown
- Habitat: Forest, rainforest
- Diet: Omnivorous
- Native Countries: China
Milne-Edwards’s Macaque Distribution
Countries
China
Tibetan Macaque Characteristics
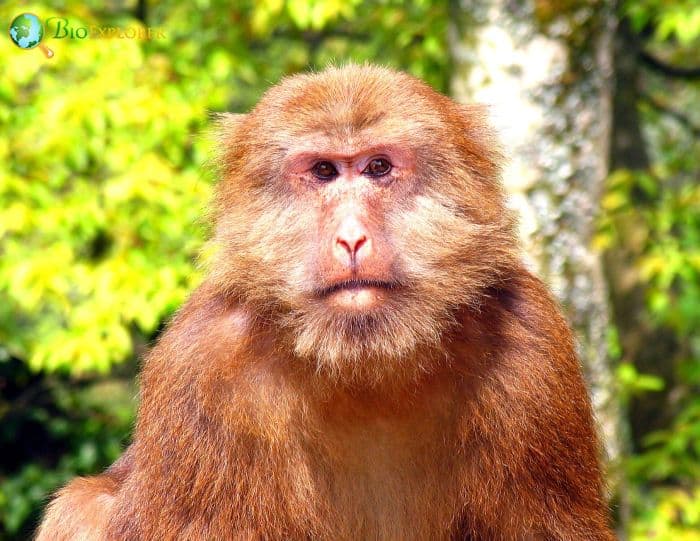

The Tibetan macaque[1] (Macaca thibetana), also called the Chinese stump-tailed macaqueor Milne Edwards macaque, is a macaque native to eastern Tibet, eastern Guangdong, and northern Shaanxi in China.
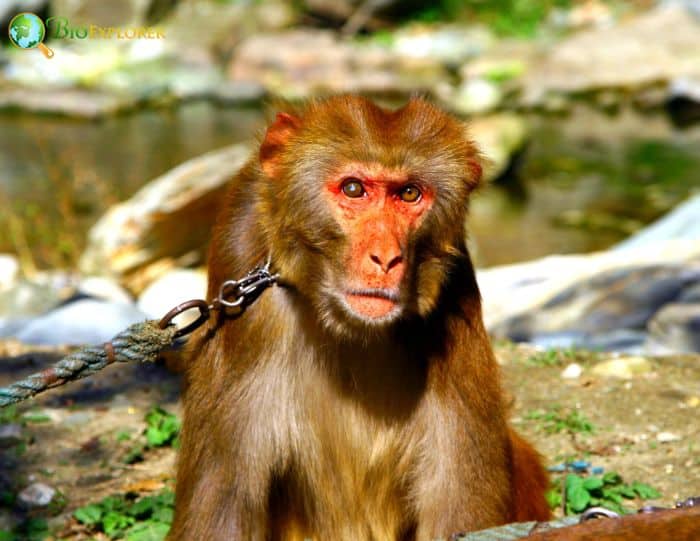

- Tibetan macaques are the largest of the macaques and have a strong, muscular build with dense fur that ranges in color from gray to brown.
- Their fur tends to lighten, even whiten, as they age. Children under two years old have much darker fur, primarily black, with white accents around the face and belly.
- They sport a lush beard and cheek hair that grows on their faces like sideburns or mustaches.
- Their faces are otherwise hairless, and coloration varies between sexes: females have paler faces that are reddish-pink, while males have paler, flesh-colored faces.
- Their eyes are large and dark brown, with expressive lids.
- One of the most notable features of this macaque species is its short tail, which has earned it the nickname “Chinese stump-tailed macaque“.
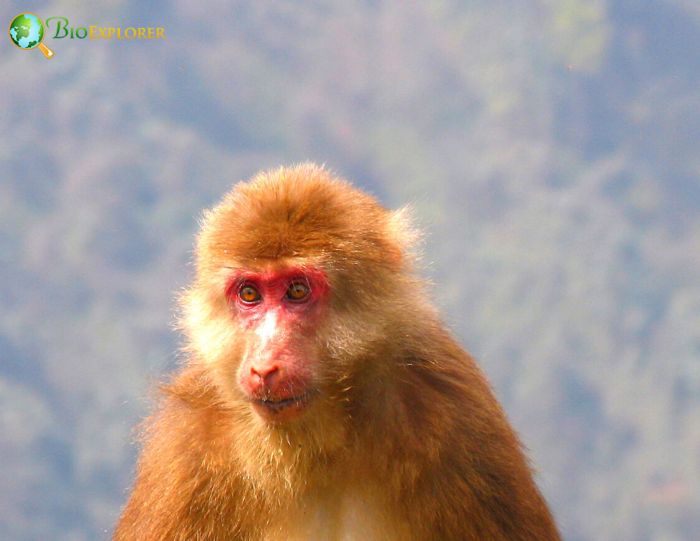

Tibetan Macaque Facts
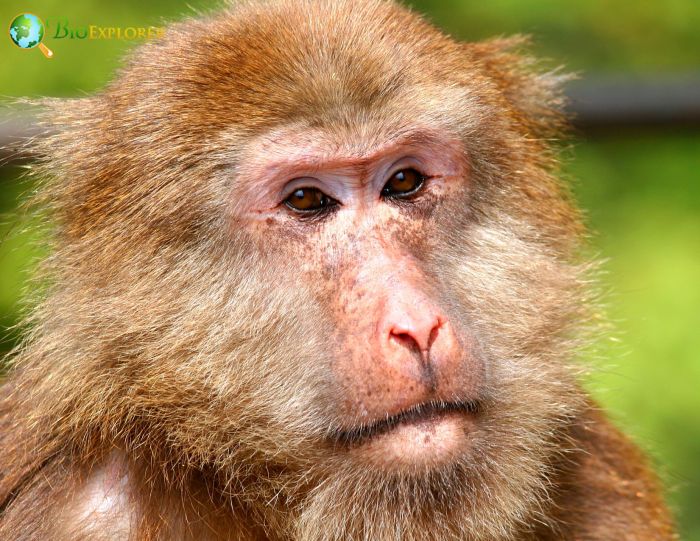

- Tibetan Macaques dwell mainly on the ground, although they are very agile and adept in trees, preferring to sleep in burrows.
- The females remain with their natal group, but the males leave after about 8 years.
- These macaques are pretty aggressive, and conflicts are shared between the Tibetan macaques and members of other species.
- Because the Tibetan Macaque is so large and aggressive, it tends to be at the top of the pecking order among primate species in its habitat.
- Tibetan Macaque groups can be as small as 10 individuals or as large as 100. These groups consist of several males and females, but there is always an established pecking order.
Suggested Reading: All Monkeys
Cite this page
Bio Explorer. (2026, January 28). Tibetan Macaque. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/tibetan-macaque/
