Japanese Macaque

| Kingdom | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animalia | Primates | Cercopithecidae | Macaca | Macaca fuscata |


- Common Names: Japanese Macaque, Snow Monkey
- Taxonomy Classification Year: 1875
- Monkey Size: 52.28 to 57.01 cm (20.58 to 22.44 in)
- Skin Color(s): Brownish gray, yellowish brown
- Habitat: Forest, mountains
- Diet: Omnivorous
- Native Countries: Japan
Japanese Macaque Distribution
Countries
Japan
Japanese Macaque Characteristics

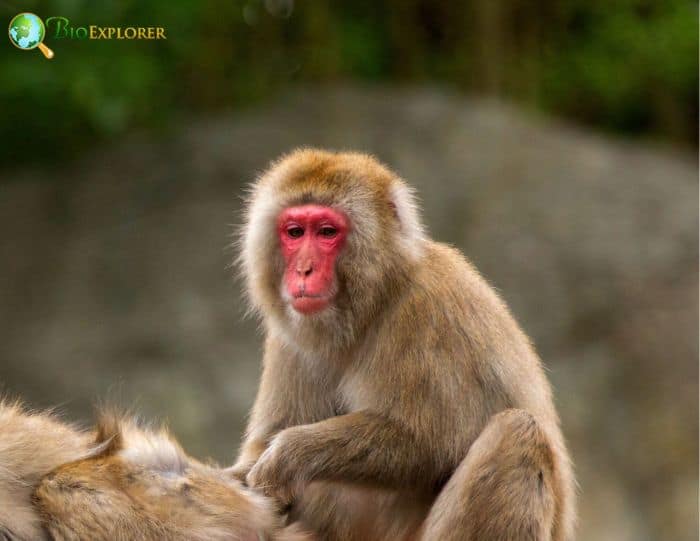
The Japanese macaque[1] (Macaca fuscata), also called the snow monkey, is a terrestrial Old World species of monkeys endemic to Japan.
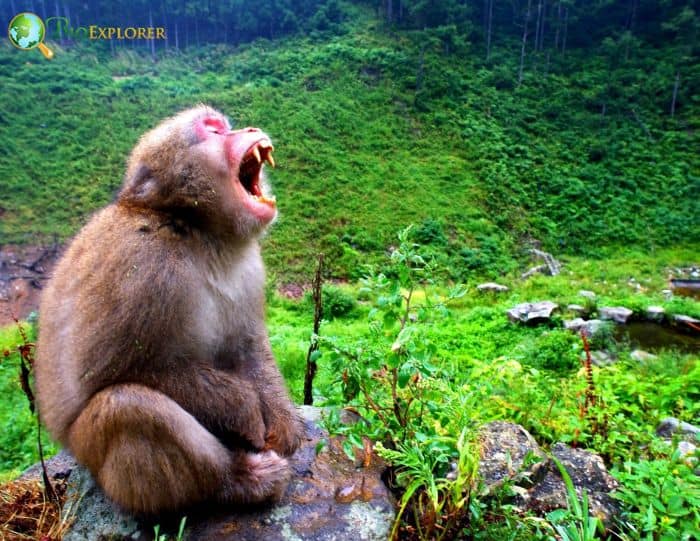
- They are colloquially known as “snow monkeys” because some live in areas where snow blankets the ground for months each year.
- No other nonhuman primate lives further north or in a colder climate. Japanese macaques range in color from shades of gray and brown to yellowish brown.
- They have colorful faces and pinkish-red rumps. Their fur is very thick, which helps them stay warm during harsh winters as they don’t hibernate.
- These Japanese monkeys have short, stumpy tails. In addition, Japanese macaques exhibit sexual dimorphism; males are typically larger and taller than females.
- Males weigh an average of 11.3 kg and measure 57 cm. Females weigh an average of 8.4 kg and measure 52.3 cm.
What Do Japanese Macaques Eat?
Japanese Macaque Facts
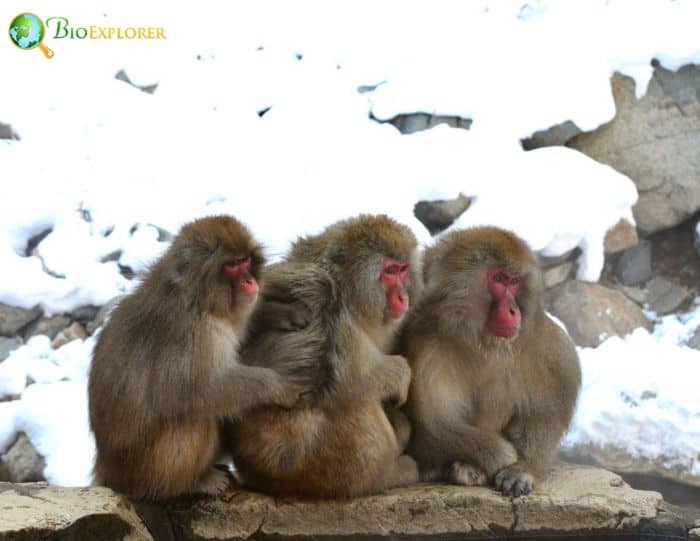

- There appears to be a correlation between the body weight of Japanese macaques and the weather.
- Japanese macaques from southern regions generally weigh less than those in northern regions of higher altitudes, where there is more snow during the winter months.
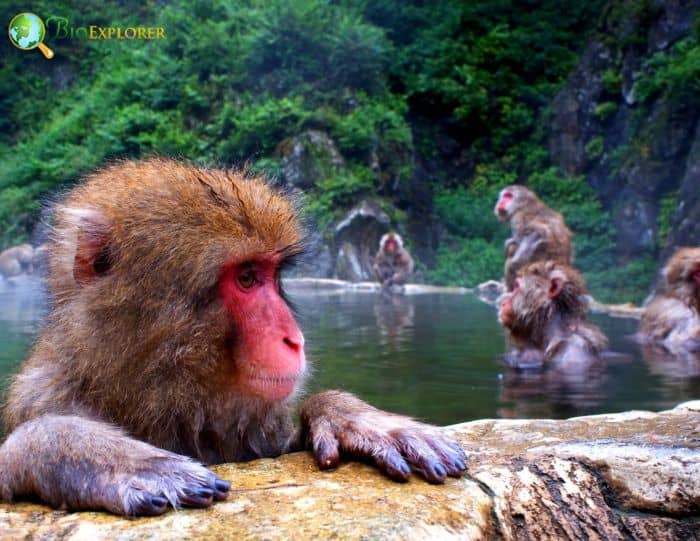
- Japanese macaques are terrestrial and arboreal and are mainly quadrupedal on the forest floor. However, they are diurnal as well.
- These macaques live in troops with a female-centric social structure.
- Hierarchical classifications are essential for the social structure of Japanese macaques. For example, high-ranking individuals have access to food first, so lower-ranking women generally eat less nutritious foods.
- Individuals emit a high-pitched voice when a predator is seen to alert other group members.

Suggested Reading: Different Breeds of Monkeys
Cite this page
Bio Explorer. (2026, January 28). Japanese Macaque. https://www.bioexplorer.net/animals/mammals/monkeys/japanese-macaque/

