Centrosome vs Centriole : The cell is the basic functional unit of life that comprises of complex structures. It goes through different phases of a cycle that enables it to grow and replicate, called the cell cycle
The cell cycle is a complex pathway that comprises of different proteins
During Anaphase, a pair of spindle fibers are formed that align chromosomes in the equatorial region of the cell to enable distribution of the chromosomes into two daughter cells.
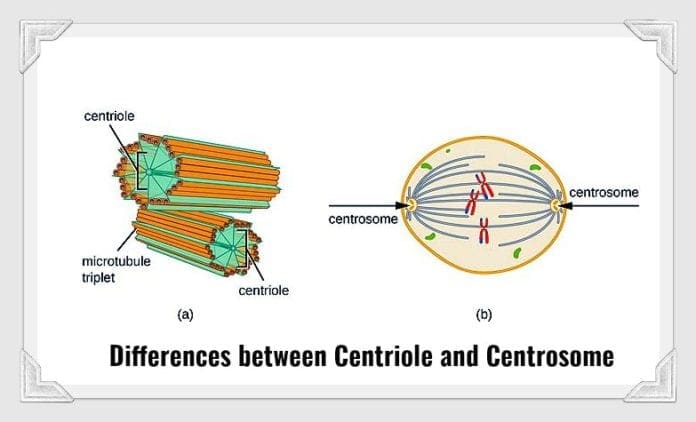
The structures that enable the formation of spindle fibers are known as centrioles , and the organelle that organizes their formation is called the centrosome .
We will discuss these terms, their difference and similarities, in more detail, within the scope of this article.
What is Centriole? Centriole “.
The Centriole is a cylindrical structure that is found in eukaryotic cells tubulin . Tubulin is a globular protein that forms microtubules. There are two pairs of centrioles in a cell, which arise as a result of centriole duplication events during cell division One centriole pair is called the mother centriole, the other is called the daughter centriole. However, the structure and arrangement of the microtubules may differ among species. Some flowering plants fungi The primary function of the centriole is to organize the spindle fibers during cell division. Another function of centrioles is in the formation of microtubules for cilia and flagella. An example of this function is sperm In some cases, defects in the centriole or mutations
What is Centrosome?
The centrosome of a cell, is the organelle which acts as the primary microtubule organizing center of the cell. It comprises of the centrioles along with a dense mass of protein known as the peri-centriolar material that surrounds it. It is an important regulator of the cell cycle. In contrast to centrioles, centrosomes come into play during prophase of the cell cycle. It is found attached to the nuclear membrane, and is released at the end of prophase when the chromosomes start to align at the equator to begin the process of mitotic spindle formation. After being released, they migrate to the poles of the cell. Each cell contains once centrosome, which replicates itself during the S phase of the cell cycle before mitosis. After cell division and cytokinesis, each daughter cell receives one copy of the centrosome. Defects in centromeres can also lead to disease such as cancer, usually caused by an abnormal number of centrosomes.
Centrosome vs Centriole Here are the key differences between Centrosomes and Centrioles:
Aspect Centriole Centrosome Definition
Centrioles are cylindrical structures that are composed of protein called Tubulin .
The centrosome is an organelle that is found in a specific region of the cell near the nuclear membrane.
Number
Centrioles are found in pairs of two in the cell, during cell division. After cell division, each cell has one pair of centrioles.
Centrosomes are found in a single pair located near the nuclear membrane at the start of the cell division process. After cell division, each daughter cell gets one copy of a centrosome.
Replication
Centrioles replicate in the S phase and two copies of a pair of centrioles are formed.
Centromeres replicate in the S phase but produce only a single copy of themselves.
Structure
Centrioles are made up of a globular protein known as tubulin. Tubulin constitutes the microtubules which are arranged in a cylindrical form.
Centromeres are regions of microtubular organization that comprise of the centrioles as well as the dense protein called peri-centriolar material.
Shape and Symmetry
Centrioles are cylindrical in shape.
Centrosomes have no definite shape and are comprised of more than one component.
Primary Function
The function of the centrioles is to form the mitotic spindle during late metaphase and early anaphase of the cell cycle. The centrioles also help in the formation of cilia and flagella that aid in movement of the sperm and ova during fertilization.
The function of the centrosomes is to provide organize the centrioles and microtubules during the process of cell division.
Types
There are two types of centrioles found among species: Atypical and typical. Typical centrioles are those with microtubules whereas atypical centrioles are those that use other structures rather than microtubules. This can be seen in the cells of the fruit fly.
Centrosome structure and type differs among species. Some species use other structures in lieu of centromeres altogether.
Diseases
Aberrant mutations in the genes encoding for the centriole can lead to defects in its structure or number. This can cause improper cell division leading to development of diseases like Meckel-Gruber syndrome. This syndrome is linked to improper assembly of the centrioles.
The formation of the centrosome may be subjected to numerical or structural aberrations. Structural aberrations can be caused due to defects in centrosome components or due to post translational abnormalities of the proteins forming the centrosome complex. Apart from structural abnormalities, numerical aberrations also occur that lead to the presence or absence of an extra copy of the centromere. Defects in centromeres are implicated in certain types of cancers.
Key Similarities between Centriole and Centrosome The centriole and centrosome also share a few common factors. The following table lists few similarities between centrioles and centrosomes.
Aspect Centriole Centrosome Functional Use
The function of the centriole is to arrange the spindle fibers in mitotic cell division.
The Centrosomes function is also centered around cell division by organizing and preparing the centrioles for cell division.
History
The centriole was discovered by Edourado van Beneden and the term Centriole was coined by Theodor Boveri.
The Centrosome was also discovered by Eduoardo van Beneden and the term Centrosome was coined by Theodor Boveri.
Occurrence
The Centriole is present in all eukaryotes
The centrosome is present in all eukaryotes but absent in plants and fungi.
The centriole and centrosome together are important and complex components of the cell division cycle that share similarities as well as differences.
Nevertheless, proper function and production of centriole and centrosome components are vital to the accurate progression of the cell cycle.
Cite This Page References Images are from Wikimedia commons under the creative commons. [1] – “Biology4Kids.com: Cell Structure: Centrioles” . Accessed September 08, 2018. Link . [2] – “Difference Between Centriole and Centrosome | Definition, Structure, Function, Comparison” . Accessed September 08, 2018. Link . [3] – “What Role Does Centrioles Play in Cell Division?” . Accessed September 08, 2018. Link . [4] – “Centrosome – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics” . Accessed September 08, 2018. Link . [5] – “(PDF) Difference Between Centriole and Centrosome” . Accessed September 08, 2018. Link .